Windows 10 comes with a lot of advanced features that are turned off by default. We have discussed one such feature in the past called Sandbox that allows users to run a virtual Windows 10 instance. Hyper-V (a feature that enables virtualization) is another such feature that is often compared with or even mistaken to be the same as Sandbox.

Hyper-V and Sandbox share some core attributes, but there are subtle differences that are important enough to understand. We will explore what virtualization is, how to enable it, and why you may use it.
Let’s begin.
What Is Virtualization
Virtualization will allow you to run other operating systems (OS) on the same machine, which is running an operating system. These are called virtual machines (VM), and Hyper-V’s job is to create virtual environment. That includes virtual hard disks to save data, virtual switches, and so on. This is also called hardware virtualization. You create a whole new computer, even multiple computers, and run them on the same machine. For example, you can now run Windows and Linux on the same computer at the same time.
Sandbox vs. Virtualization
A sandbox will also create a virtual space, but you can only install and test apps and software. It will not create virtual hardware. It’s not simulating an entirely new computer environment but shares the same hardware and drivers as your primary installation.
Because the sandbox is dependent on the primary machine’s hardware, any app you install, files you create, and settings you change will vanish the moment you close the sandbox. Shutting down the computer will yield the same result. It depends on the primary installation’s hardware resources to exist, just like an app. That makes it an excellent place to test apps and settings without running the risk of messing up your primary installation.

VM acts and behaves like a real computer, and whatever you do inside VM remains in the VM. You can’t access it outside of it in the primary installation. But, a VM is not temporary. It will save itself when you put the computer to sleep or even when shut down it . That means it is more permanent, allowing you to do much more than just test apps. You can work on it, create and save files inside it, and test or troubleshoot or even build something. My friend used to practice Oracle modules inside a VM on his laptop.
Leo from Ask Leo has done an excellent job of explaining the difference using flowchart and diagrams.
Why Use Virtualization
There are a few scenarios where it may come in handy like:
- Install Linux or another OS that is not Windows
- Run older versions of Windows like 7, XP
- Create/remove OS on the fly with no footprint
- Build and test apps in different environments
Not all apps will work in virtualization. For example, games that depend on hardware like graphics card won’t run in a virtual environment.
System Requirements
System resources will depend on the number of virtual instances you are running and what you are doing inside them. These are the minimum requirements:
- Windows Pro or Enterprise license
- At least 4GB RAM
- 64-bit processor with SLAT and VM Monitor Mode Extension
- Enable Virtualization Technology in BIOS – name may differ based on make and model of the motherboard
- Enable Hardware Enforced Data Execution Prevention in BIOS
Entering BIOS is easy on Windows 10, so you don’t have to worry about that.
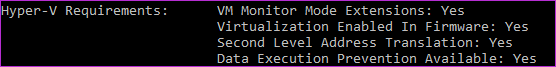
Now, open CMD and type systeminfo command to ensure your system meets all the hardware requirements. You should view Yes in front of all entries next to Hyper-V Requirements.
How to Enable Virtualization
The steps for enabling virtualization in Windows 10 is pretty much the same as enabling the sandbox mode. You need to tick the right box, and you are done.
Step 1: Open Control Panel from the Start menu.
Step 2: Search for and open Turn Windows features on or off.
Step 3: Select Hyper-V in the pop-up that follows. It should have two sub-folders as you would notice in the screenshot below.

Save everything. You will find Windows Sandbox option in the same menu. You can enable that too at the same time. It’s not an either/or feature.
You can also enable Hyper-V using Command Prompt or PowerShell.
Life in a Simulation
The virtualization or Hyper-V feature is designed with pro users, enthusiasts, developers, and programmers in mind. That’s one reason why it is not available to Home users. Enabling the feature itself is pretty easy and takes less than a few moments. While the system requirements are pretty low, I would recommend you to beef up your computer with an extra RAM stick. That will keep both the primary and virtual installation/s happy and working smoothly. So, what are you using it for?
Next up: Windows Sandbox and Sandboxie offer a risk-free means to test out programs. Check out how they stack against each other.
Was this helpful?
- Update or re-install the biometrics driver using the Device Manager tool on your PC.
- Delete your fingerprint, and register it again in Windows Hello settings.
- Open the Services program, and restart the Windows Biometric Service.
Basic Fixes
- Restart PC: Restart your PC to fix any temporary bugs and glitches.
- Clean your finger and the sensor: The biometrics sensor on your PC will not work if it is dirty, or if your finger isn’t clean.
- Update PC: Update your PC to the latest available version of Windows for a bug-free experience.
- Check for malware: Using Windows Defender , scan for malware that may be causing the problem.
Fix 1: Update or Reinstall the Biometrics (Fingerprint) Driver
The software drivers for the biometrics hardware on your Windows PC may be outdated and are due for an update. The update can fix bugs and problems that you are facing with the Windows Hello fingerprint service. Additionally, if the biometrics driver was installed through a corrupt package, it may cause issues with Windows Hello.
Therefore, updating or reinstalling these drivers will help.
Step 1: Open Device Manager from the start menu.
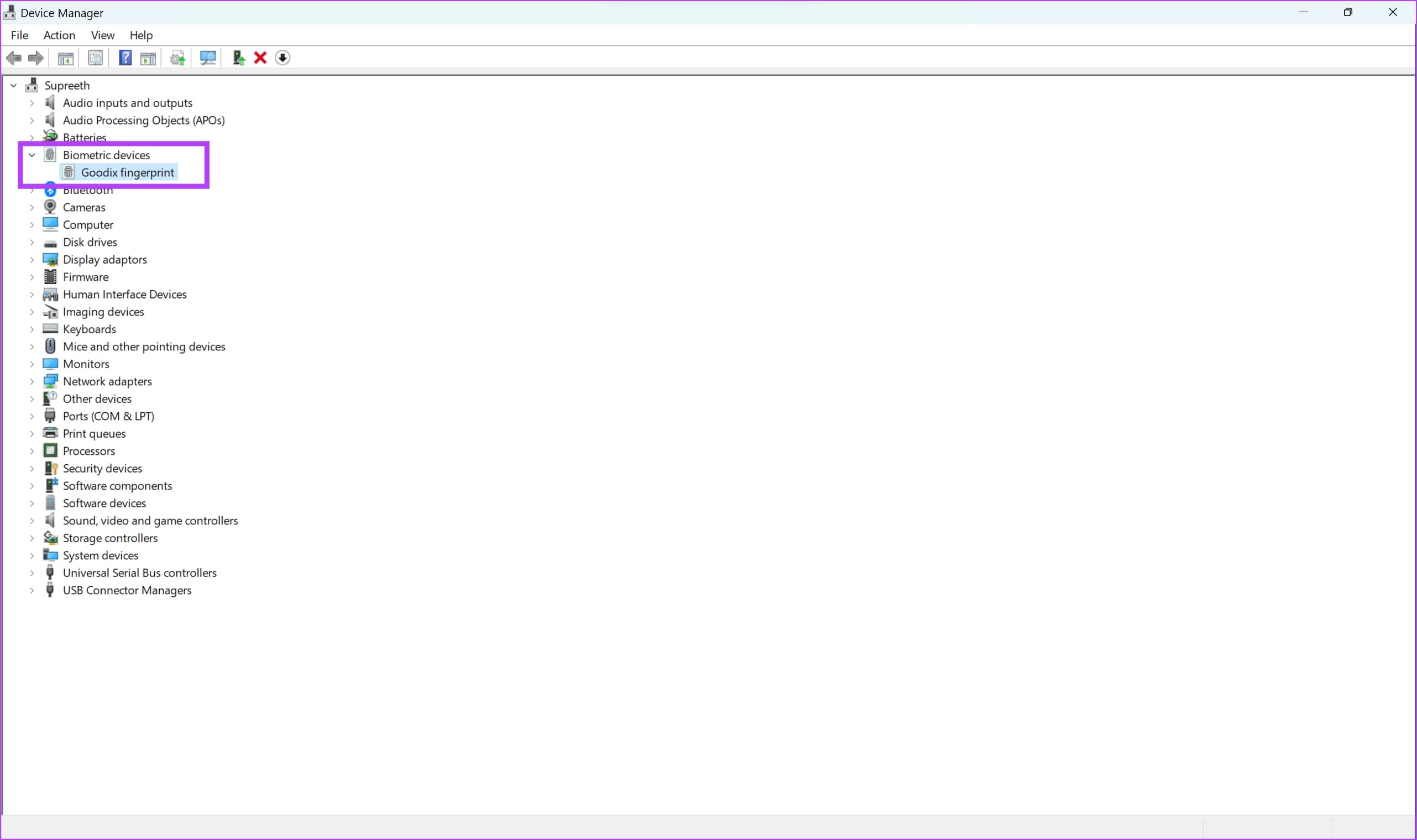
Step 2: Click to expand Biometric Devices .
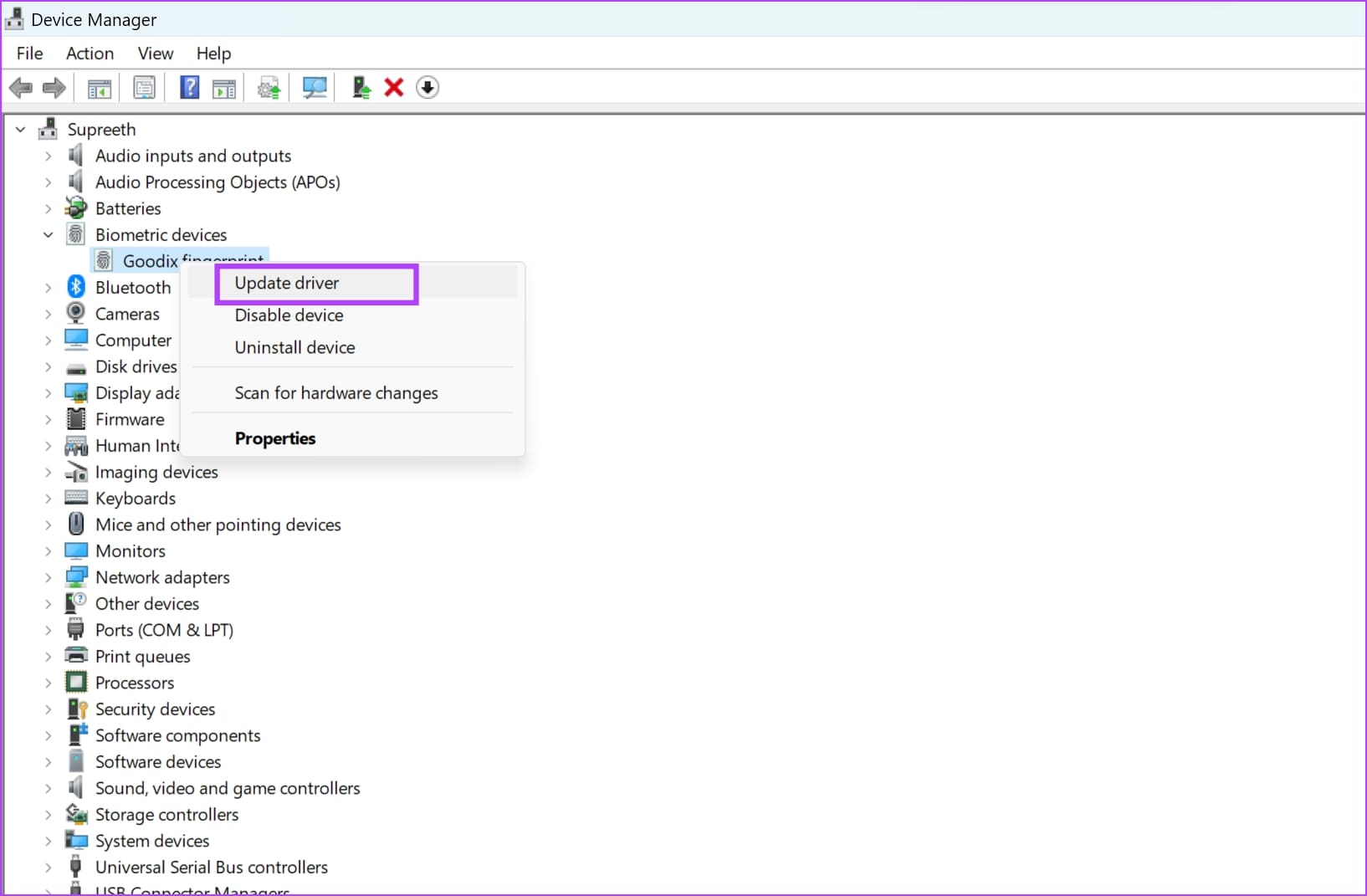
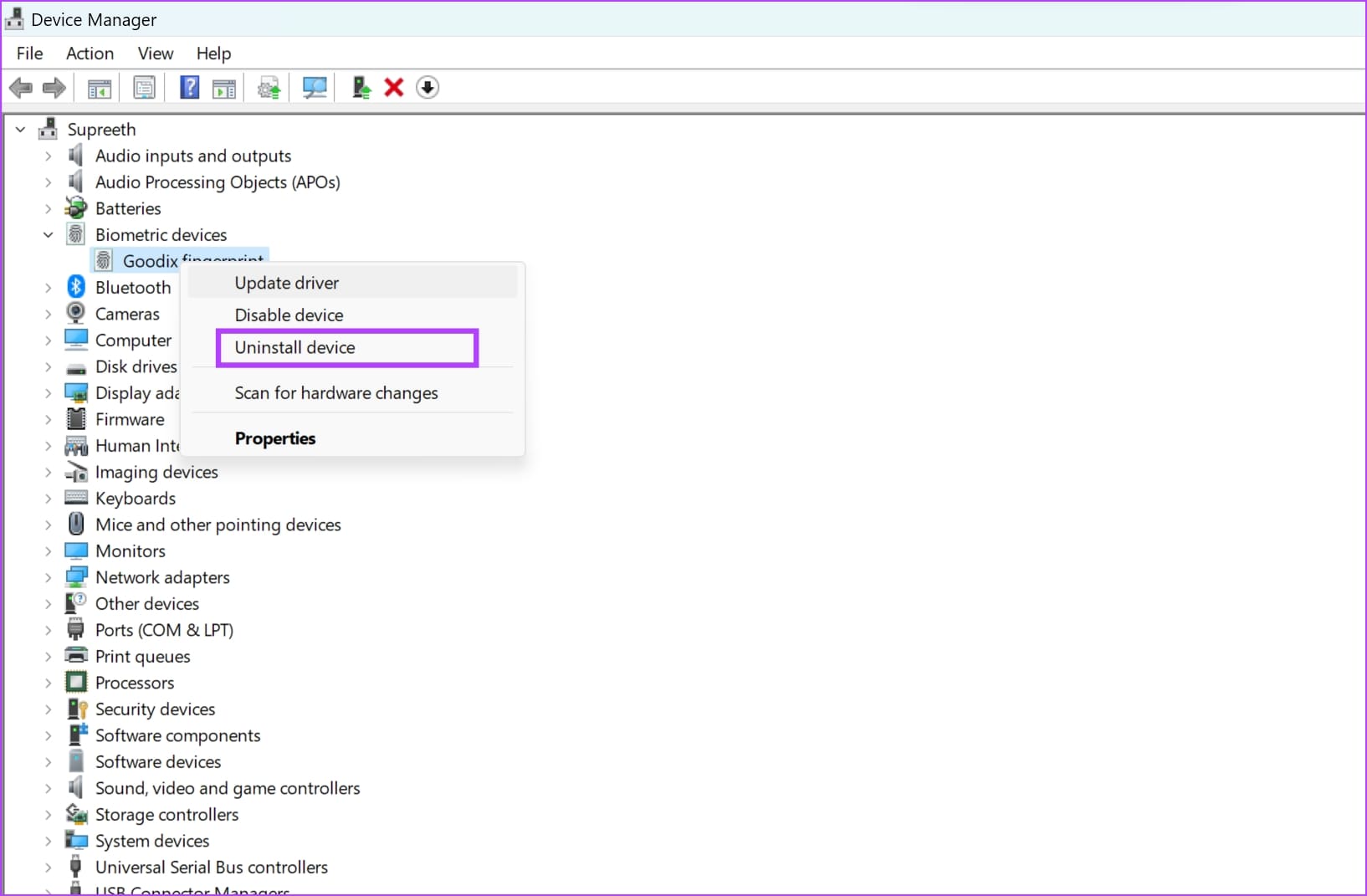
Step 3: Right-click on the biometric device and click on Update driver .
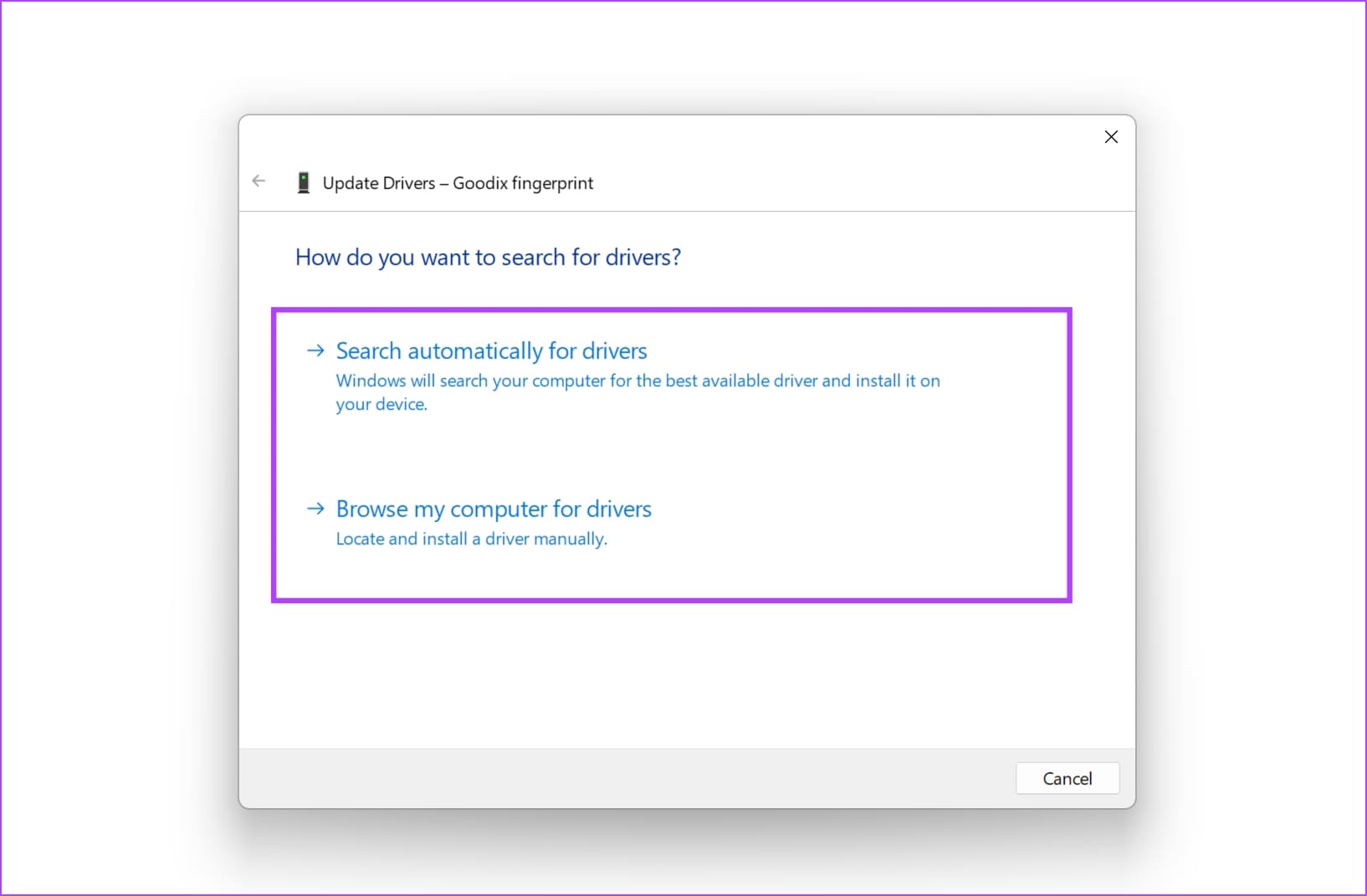
Step 4: Choose whether you want to browse the update file locally or, let Windows search the internet for the same.
If you want to re-install the driver, click on Uninstall Device , confirm your action, and restart your PC to automatically install the driver.
Fix 2: Re-Register Your Fingerprints
If the saved fingerprint on your PC is corrupted, removing it and registering your fingerprint once again will help.
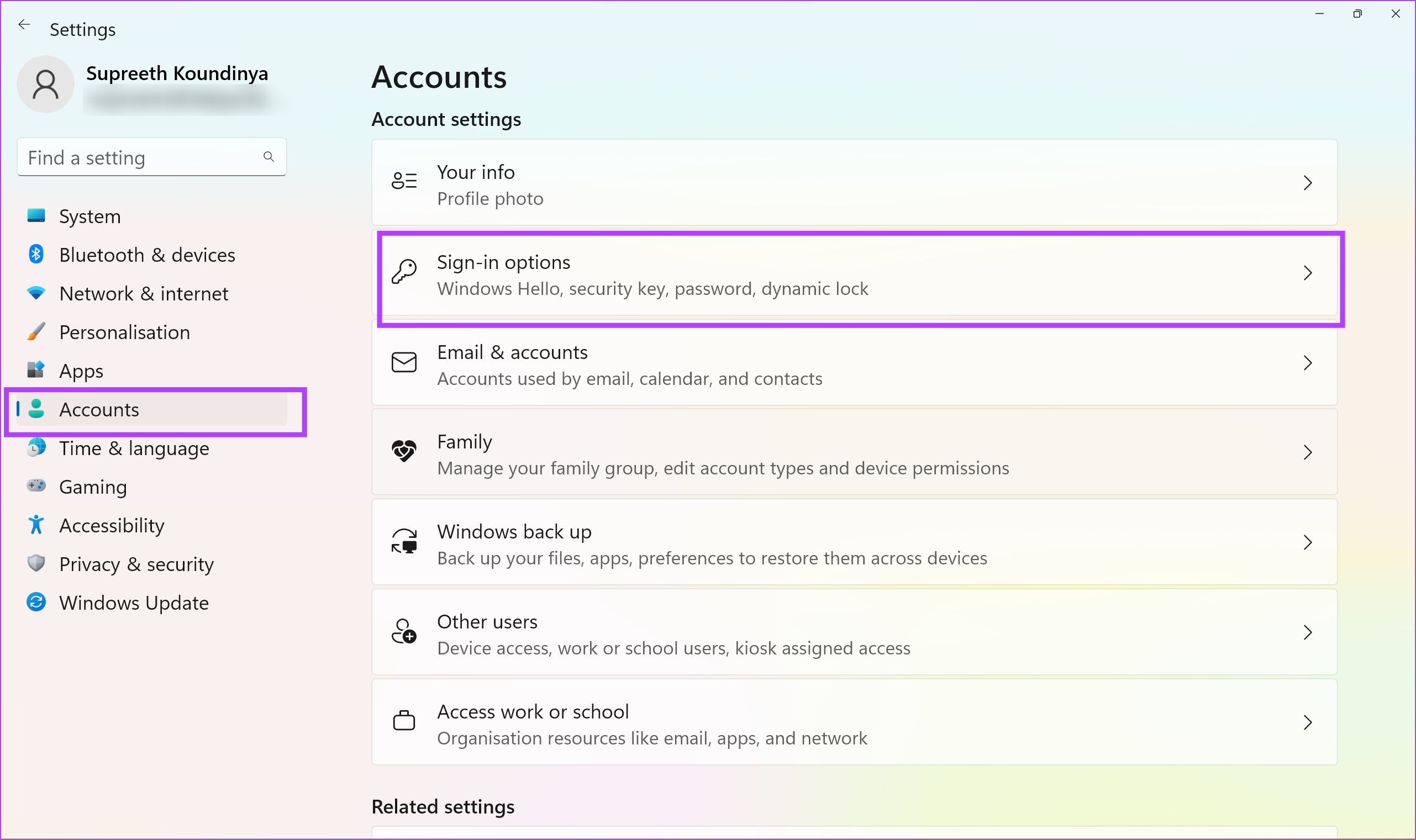
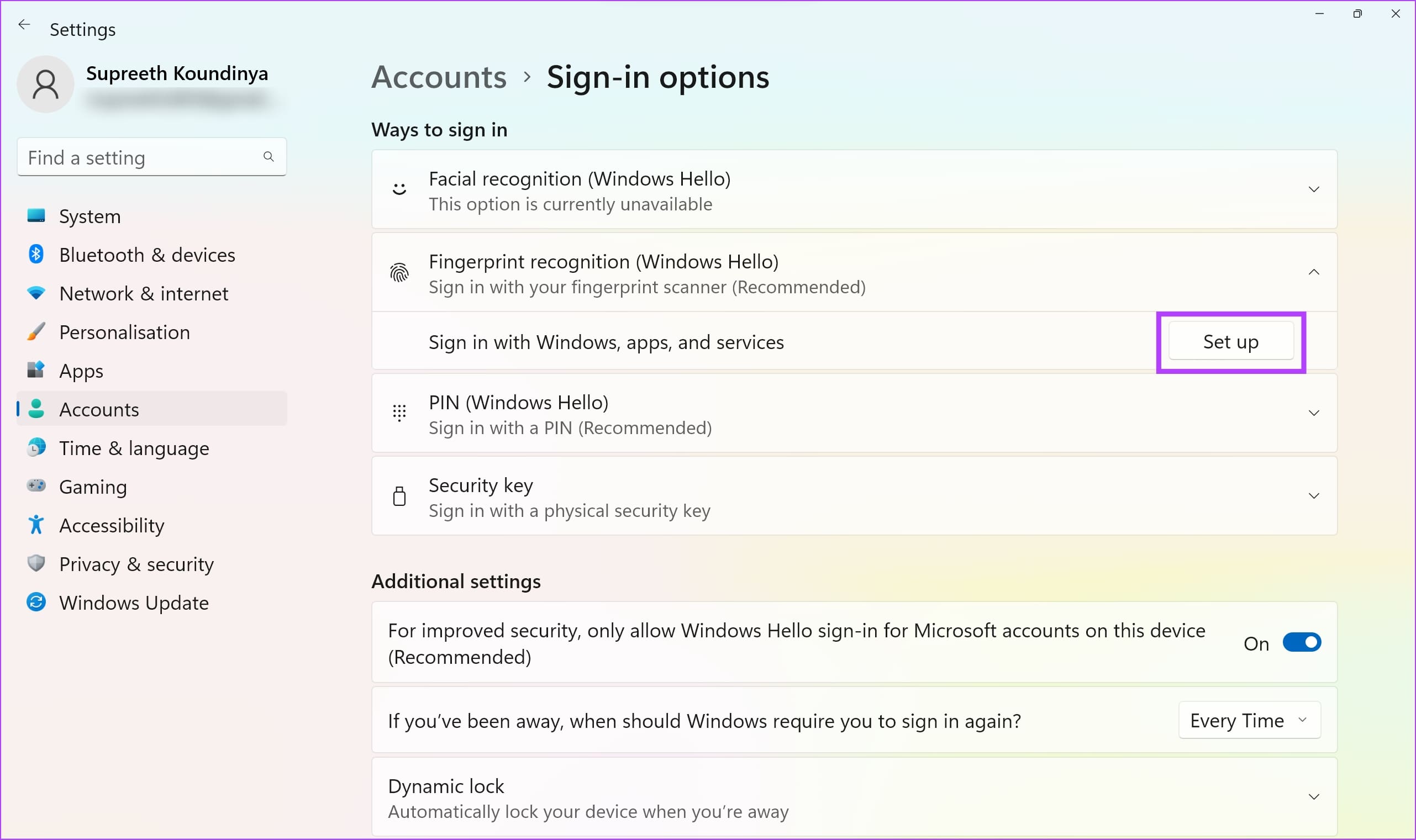
Step 1 : Open the Settings app on your PC.
Step 2: Select Accounts in the sidebar and click on Sign-In Options .
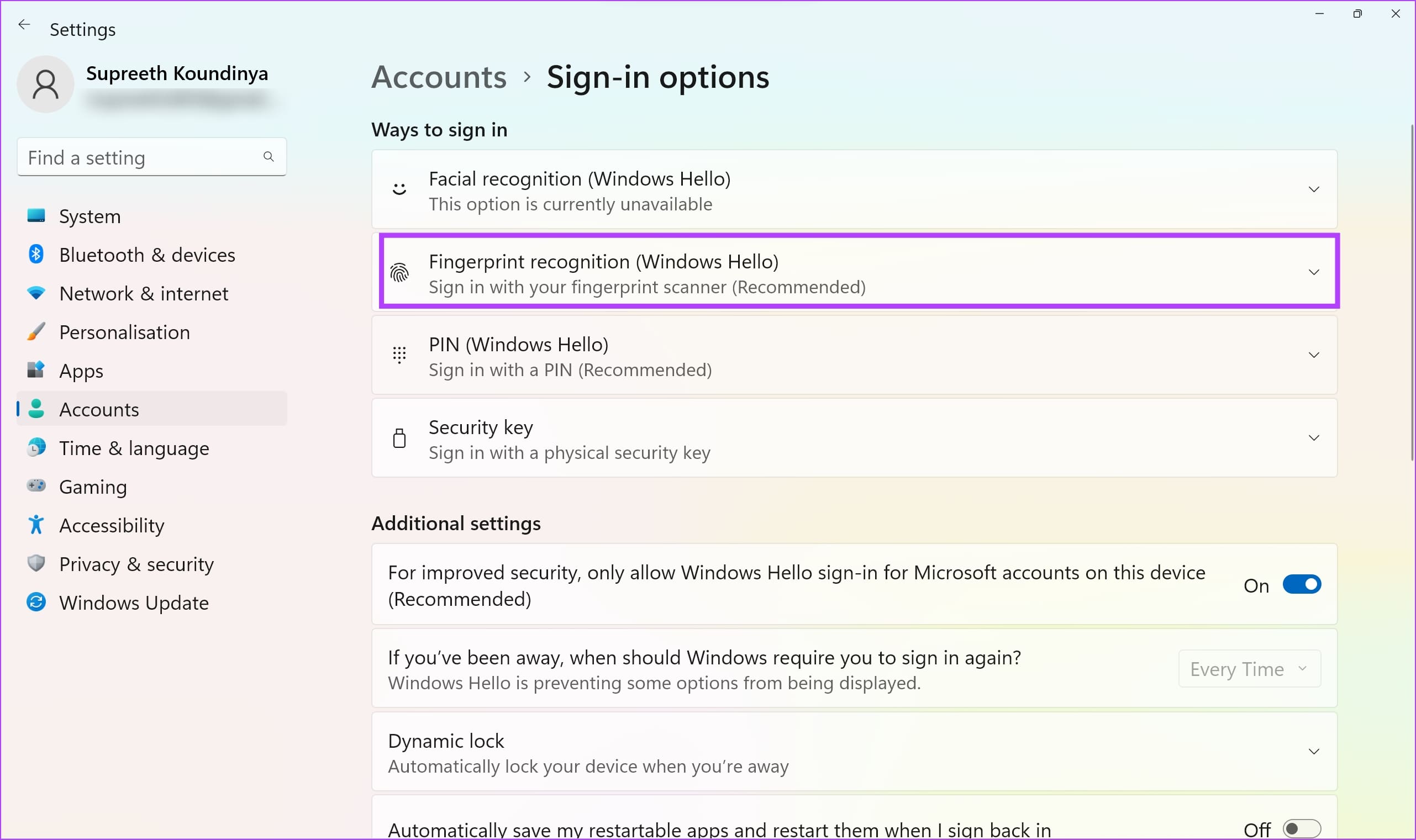
Step 3: Click on Fingerprint Recognition .
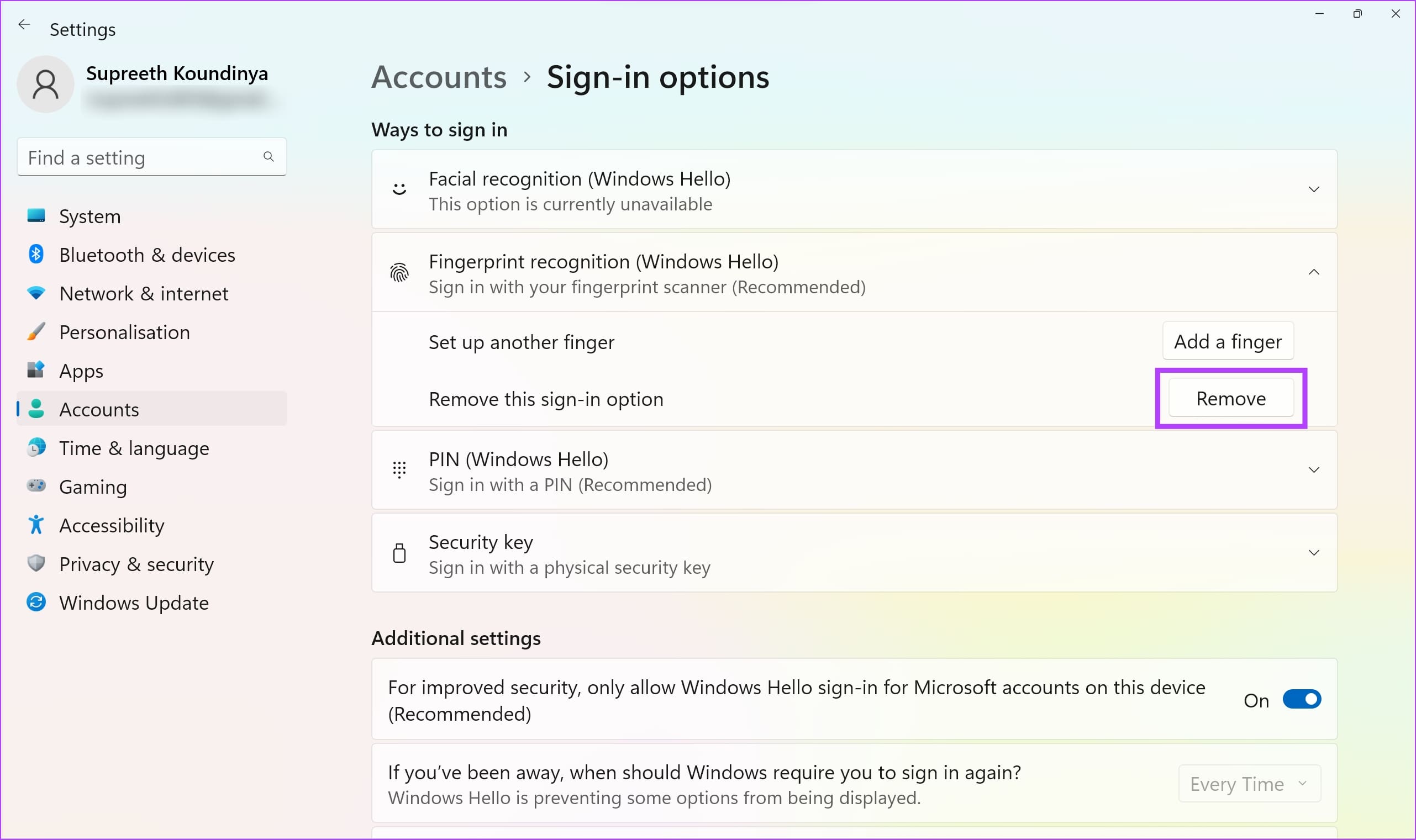
Step 4: Click on Remove to delete the registered fingerprint.
Step 5: Now, click on Set Up , and register your fingerprints once again.
Fix 3: Start Biometrics Service Automatically
If the Windows Biometric service – a process that is required to activate the fingerprint sensor on your device does not start up every time you boot up your PC, you may encounter problems with Windows Hello.
Step 1: Open the Services application from the Start menu.
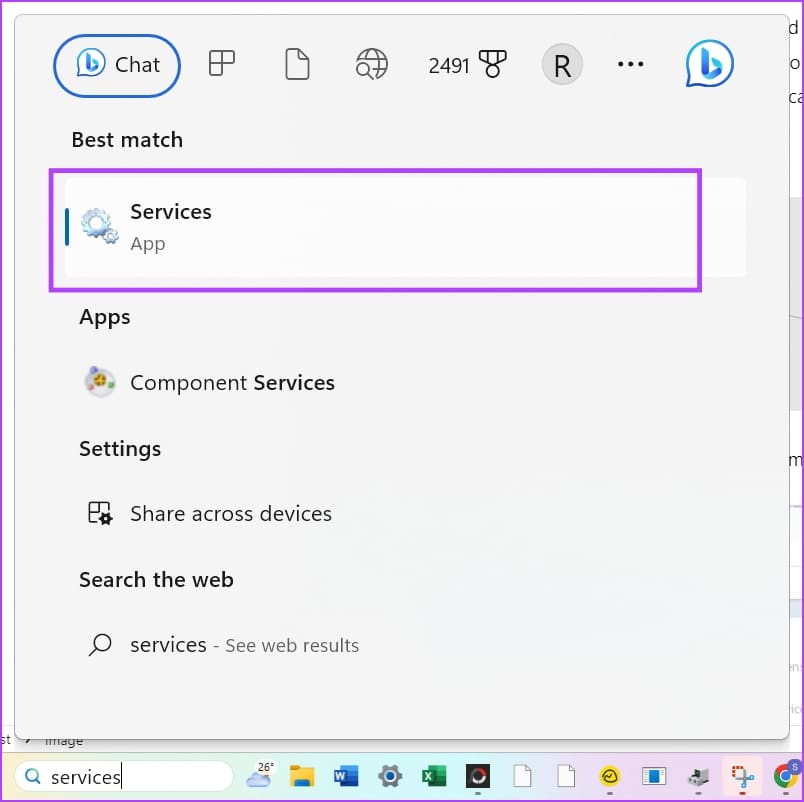
Step 2: Scroll down to find, and right-click on Windows Biometric Service .
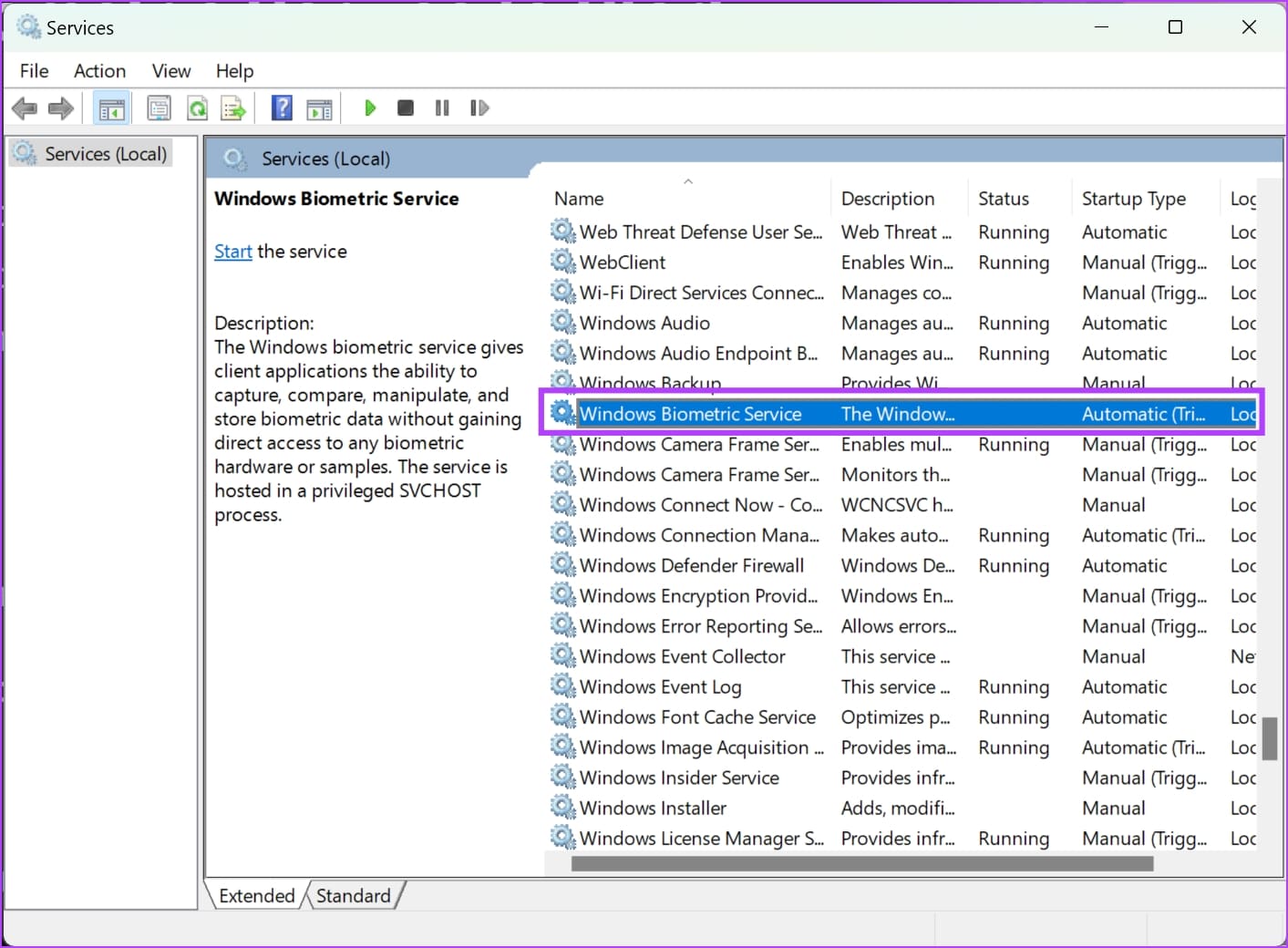
Step 3: Click on Properties .
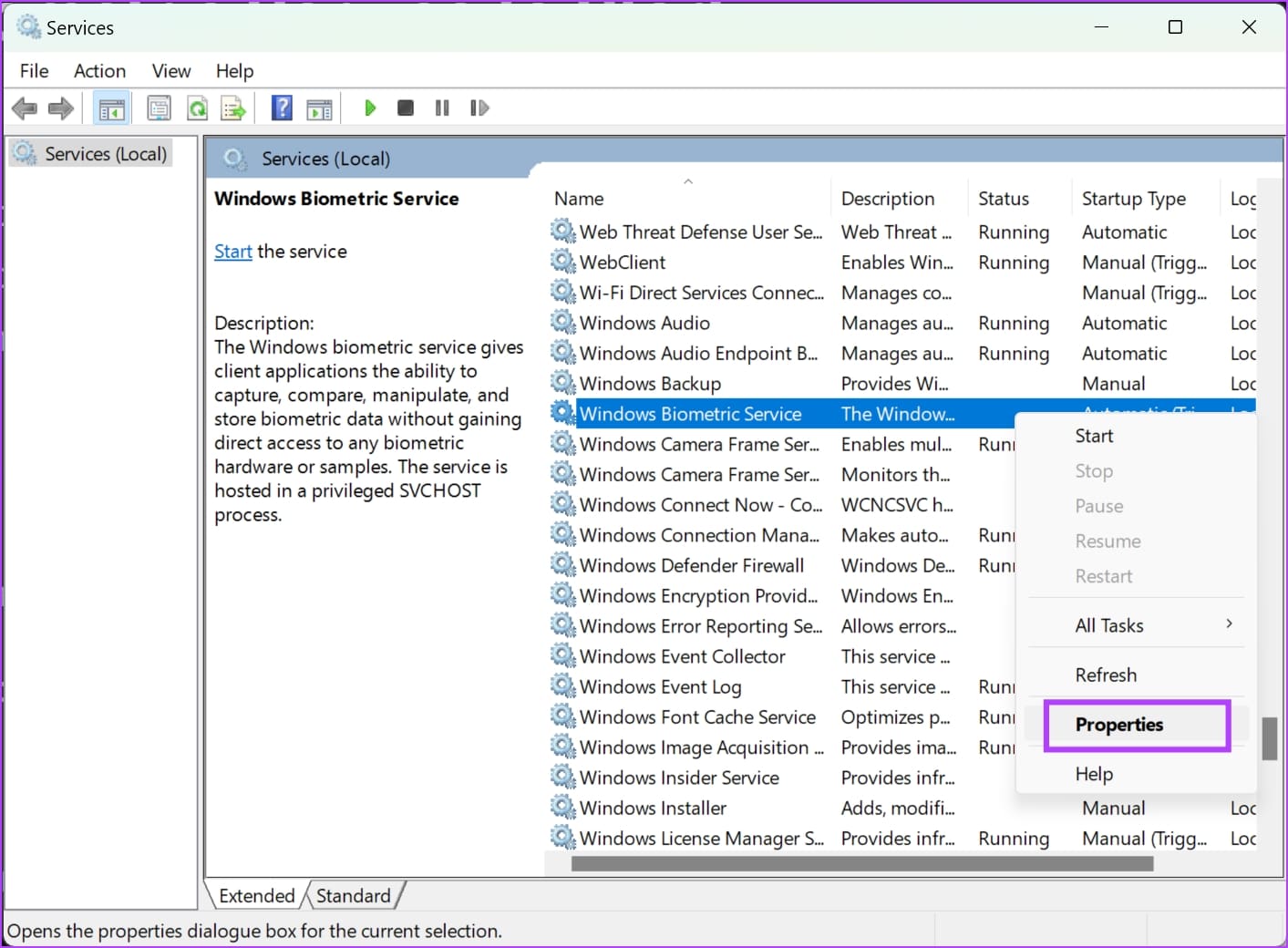
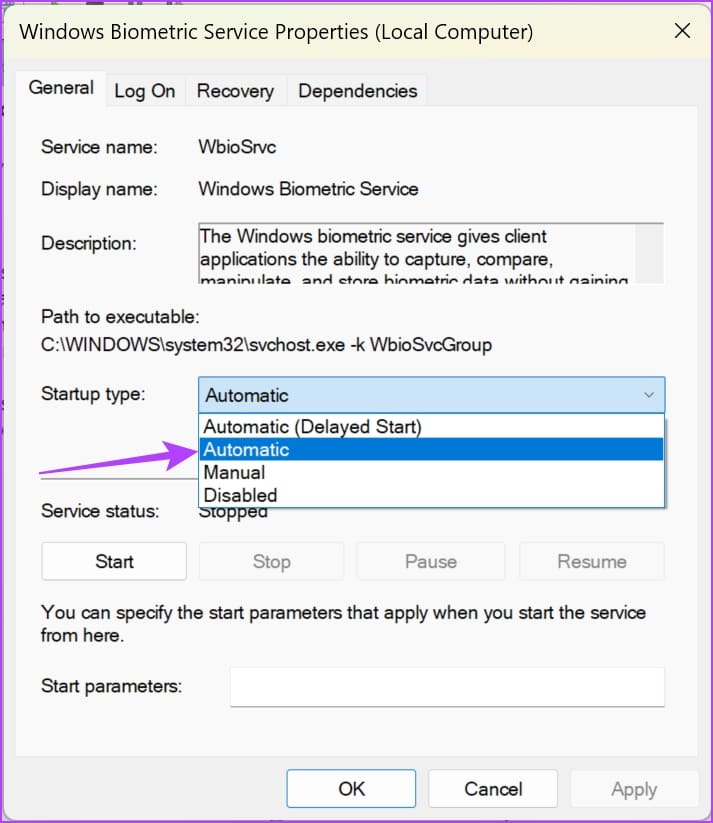
Step 4: Open the dropdown menu for Startup type , and click on Automatic . Click on Apply and OK to confirm your changes.
Fix 4: Reset WinBio Database
Your Windows PC stores all the biometrics data in the WinBio database. If any entry is corrupted, it may be responsible for the error message.
Step 1: Open the Services application from the Start menu.

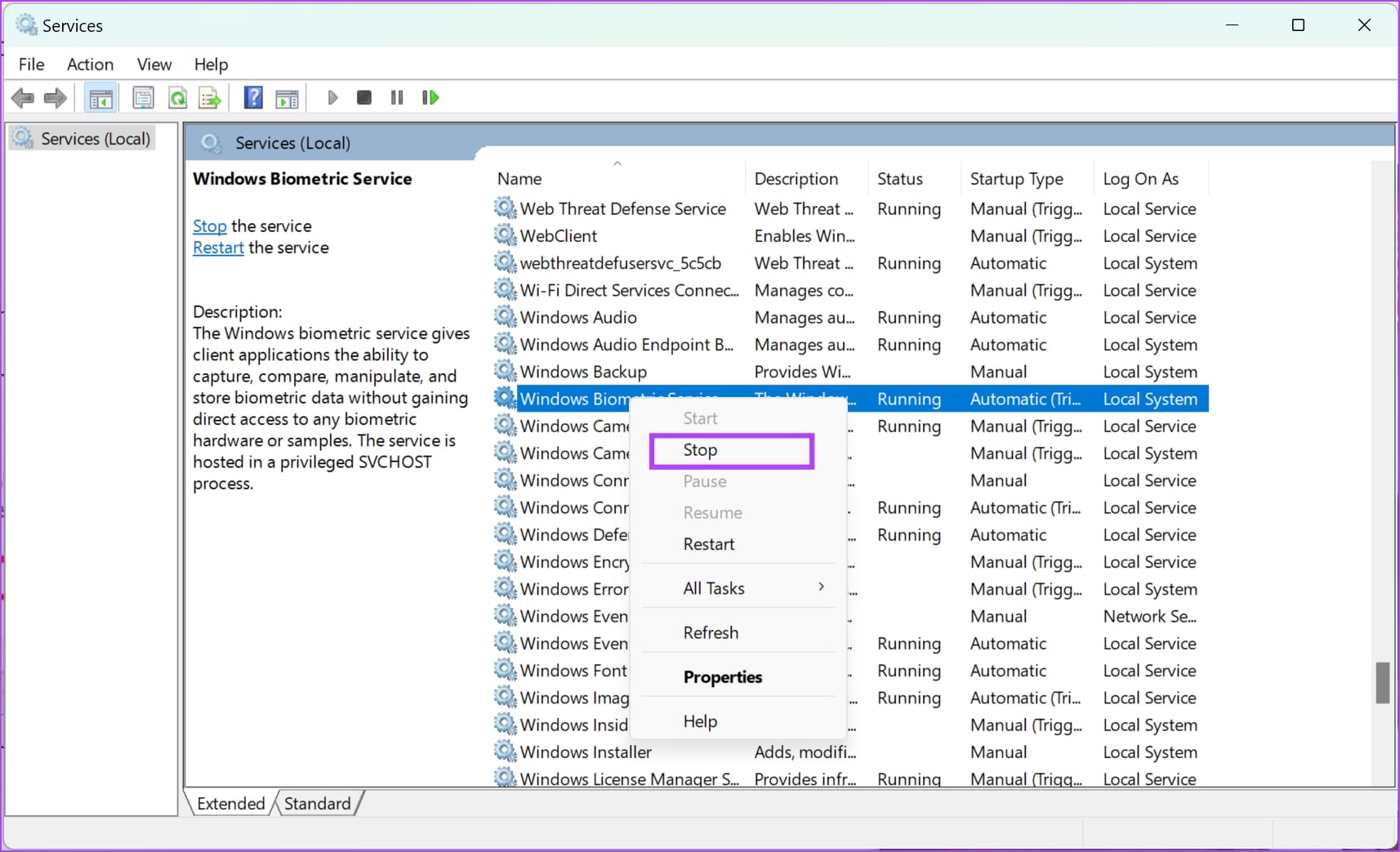
Step 2: Scroll down to find, and right-click on Windows Biometric Service .

Step 3: Click on Stop .
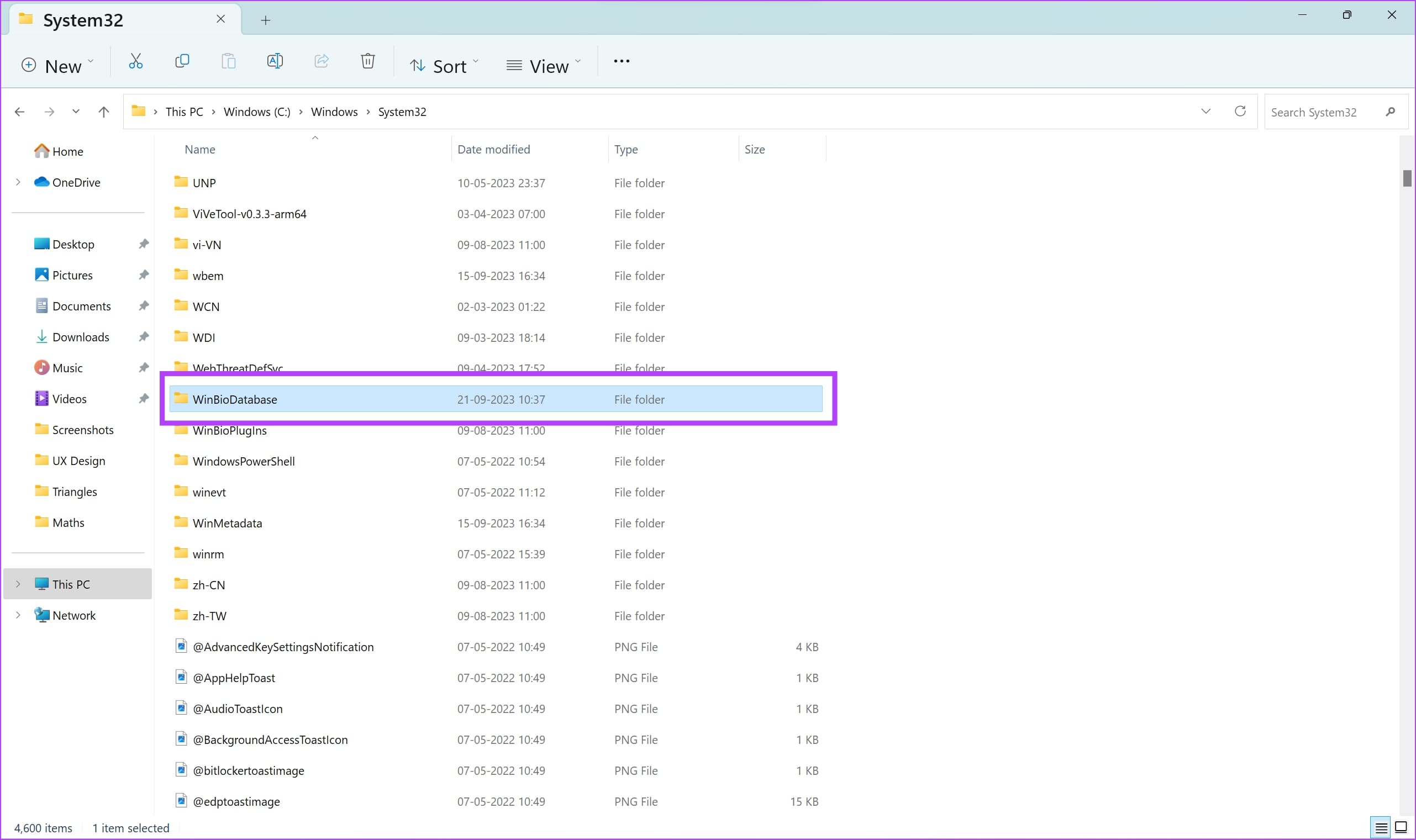
Step 4: Now, navigate to This PC -> Windows (C:) -> Windows -> System32 and open the WindBioDatabase folder.
Step 5: We will have to delete all the files present here.
But we recommend taking a backup . Select all files. Copy and paste them onto a different location.
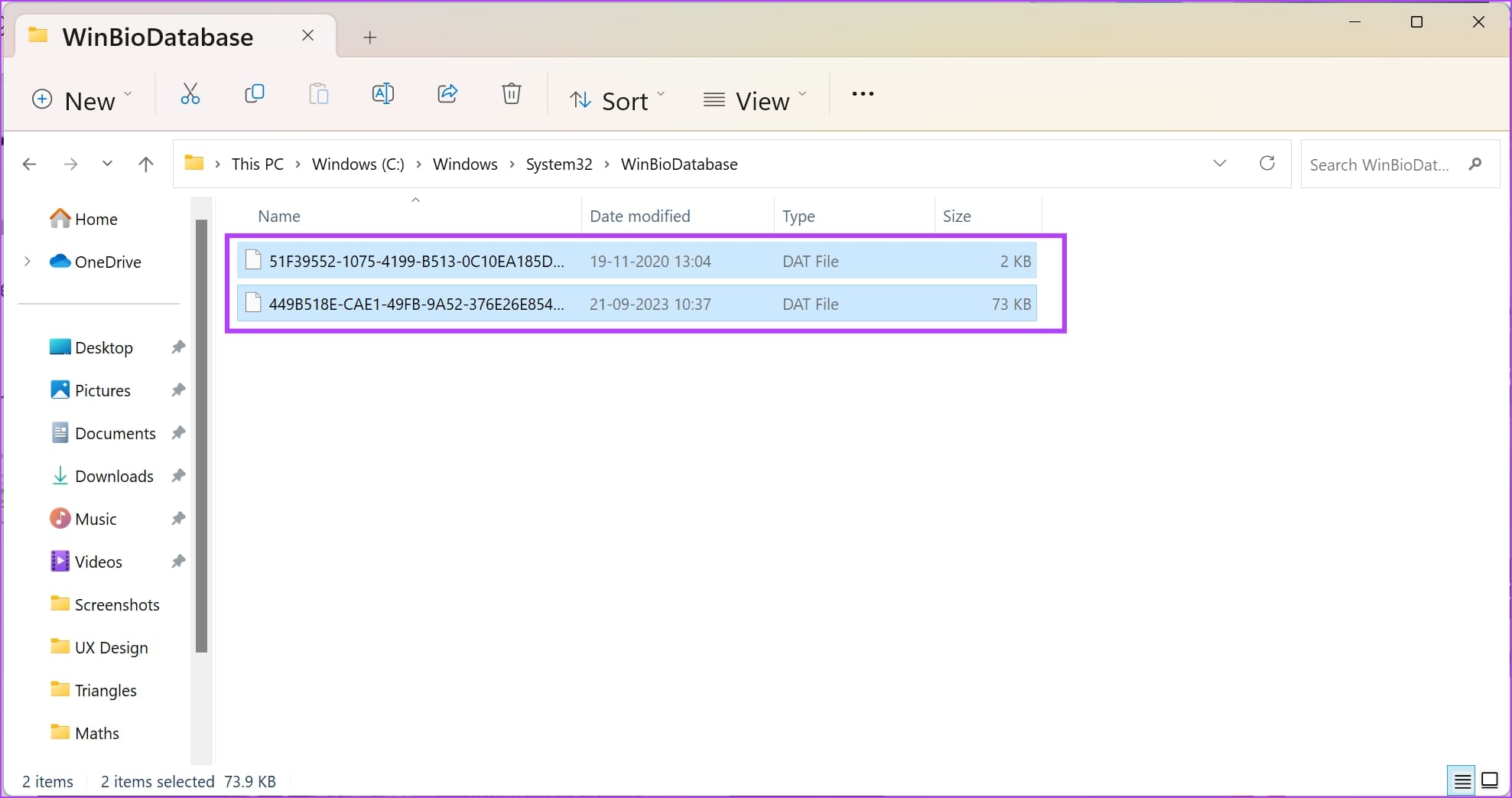
Step 6: Once you have created a copy of all the files in a different destination – go ahead and delete the files .
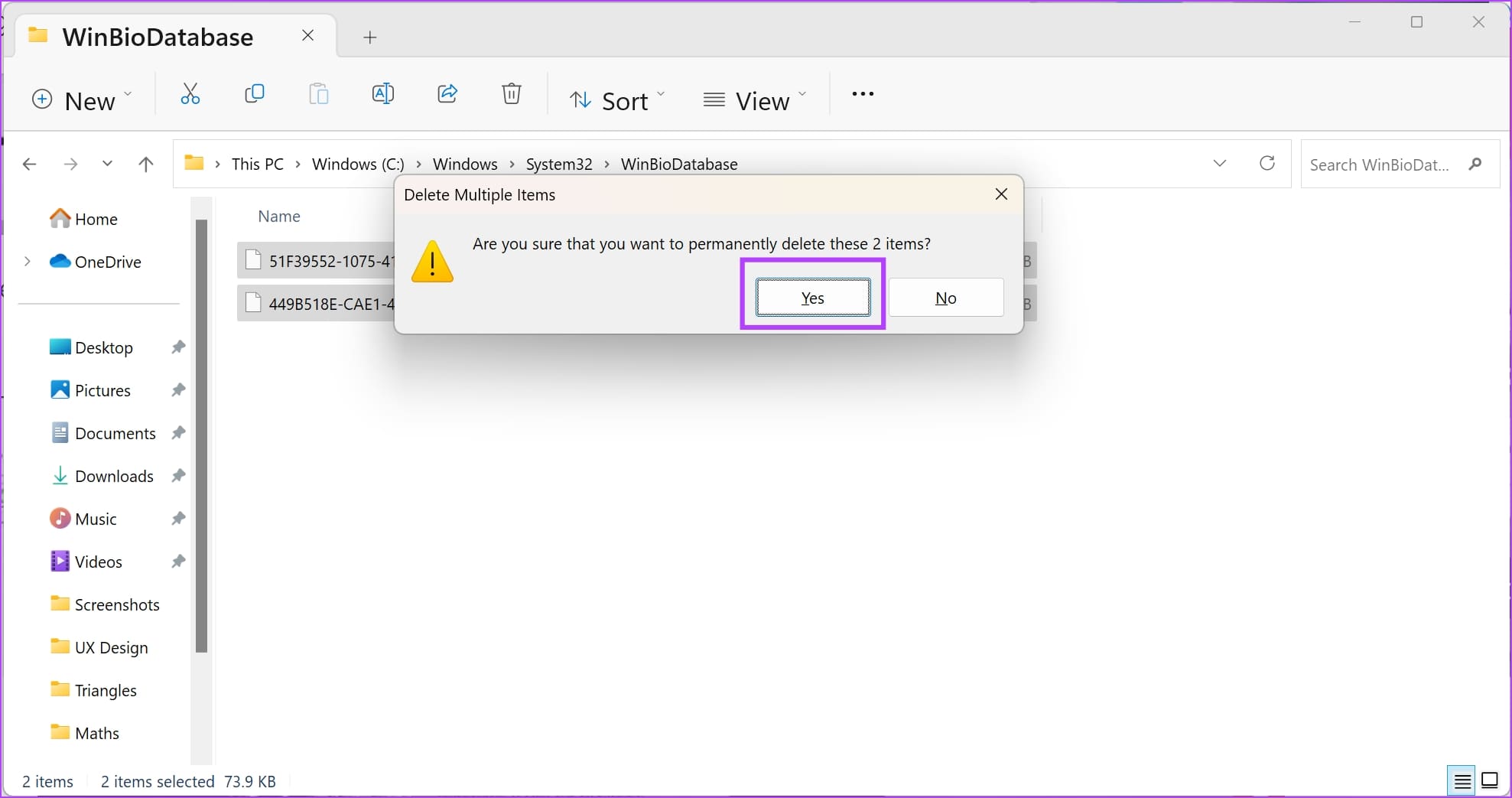
Step 7: Now, go back to Windows Services , right-click on Windows Biometric Service , and click on Start .
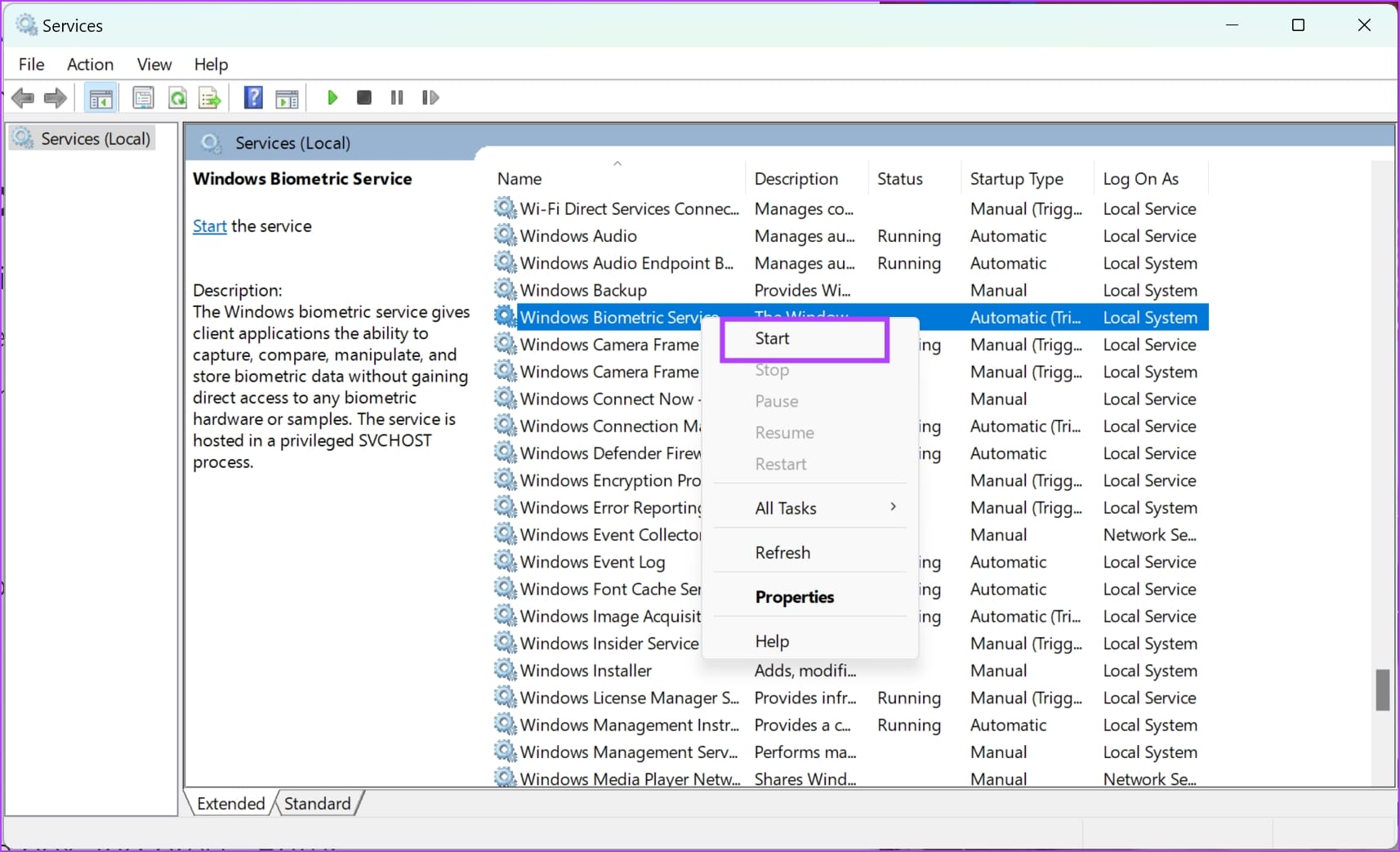
Once you restart the biometric service, you must register your fingerprint again in the Settings app. Refer to the ‘Fix 2’ section to register your fingerprint.
Fix 5: Edit the Registry
If the biometric login is deactivated via the Registry on your Windows PC, you can enable it by using the registry editor.
Step 1: Open the Registry Editor from the Start menu.
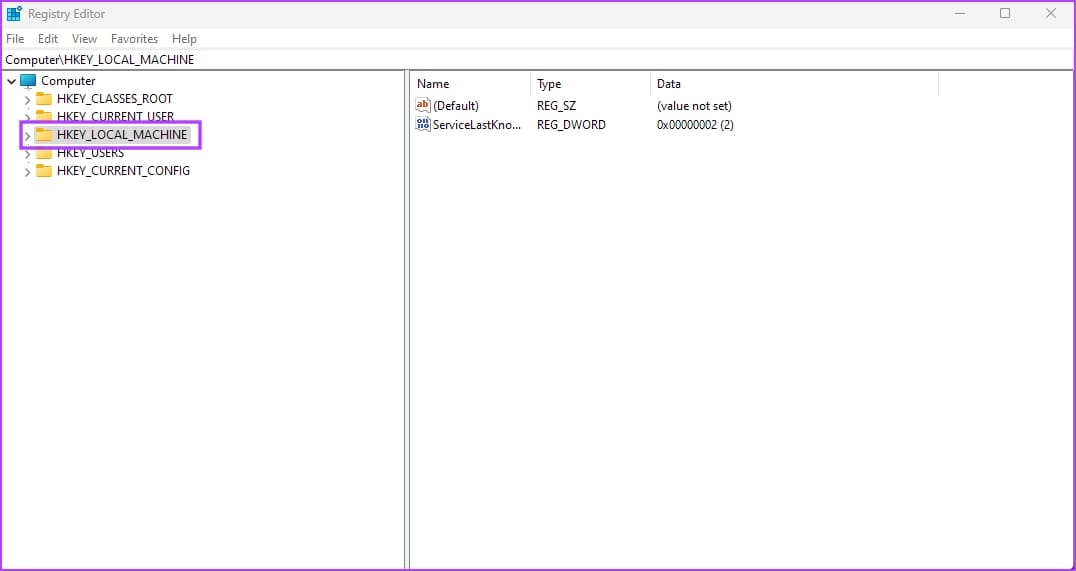
Step 2: Select the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE folder.
Step 3: Click on SOFTWARE .

Step 4: Click on Policies -> Windows -> and right-click on System .
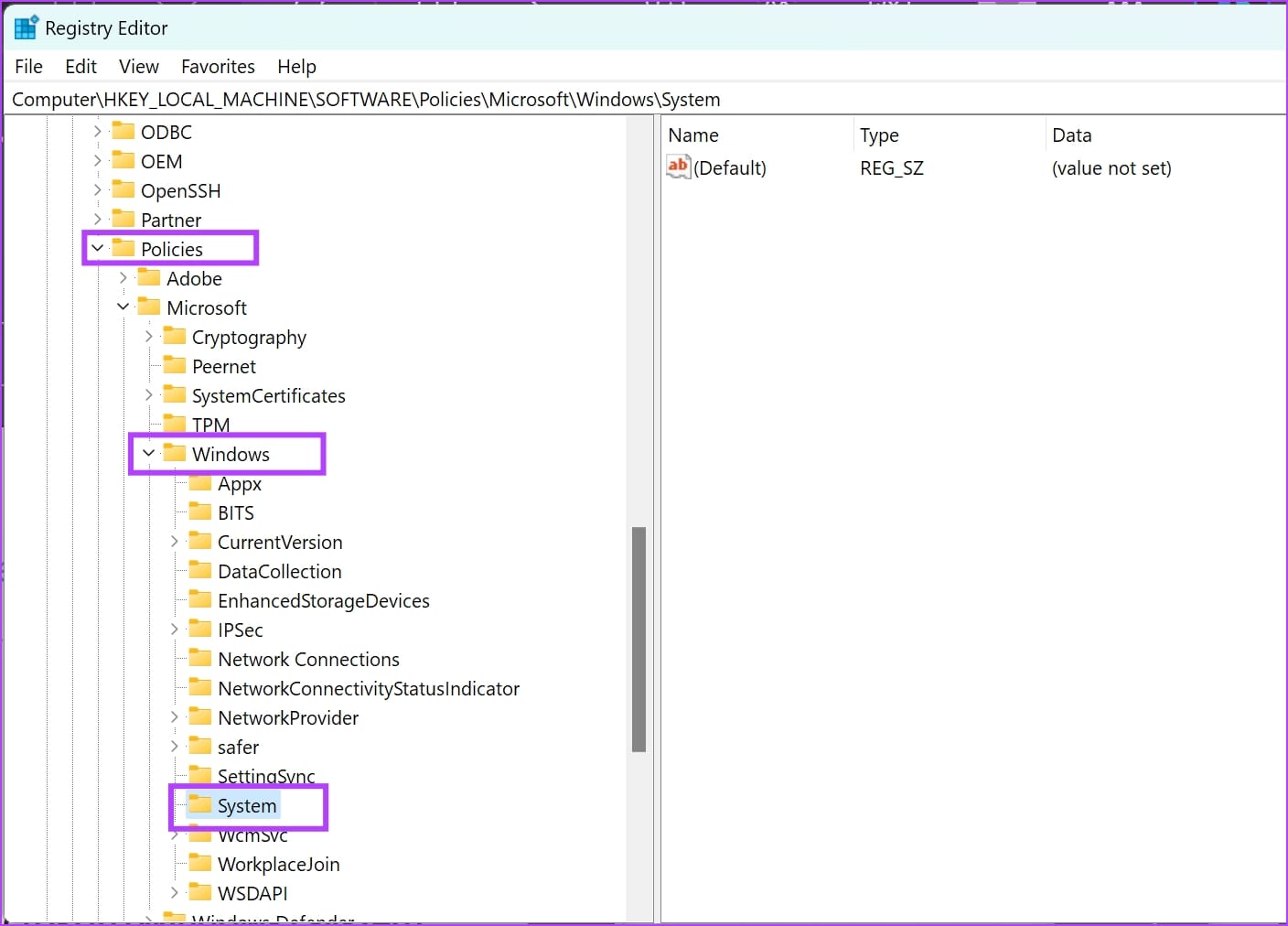
Step 5: Click on New -> DWORD (32-Bit) Value .
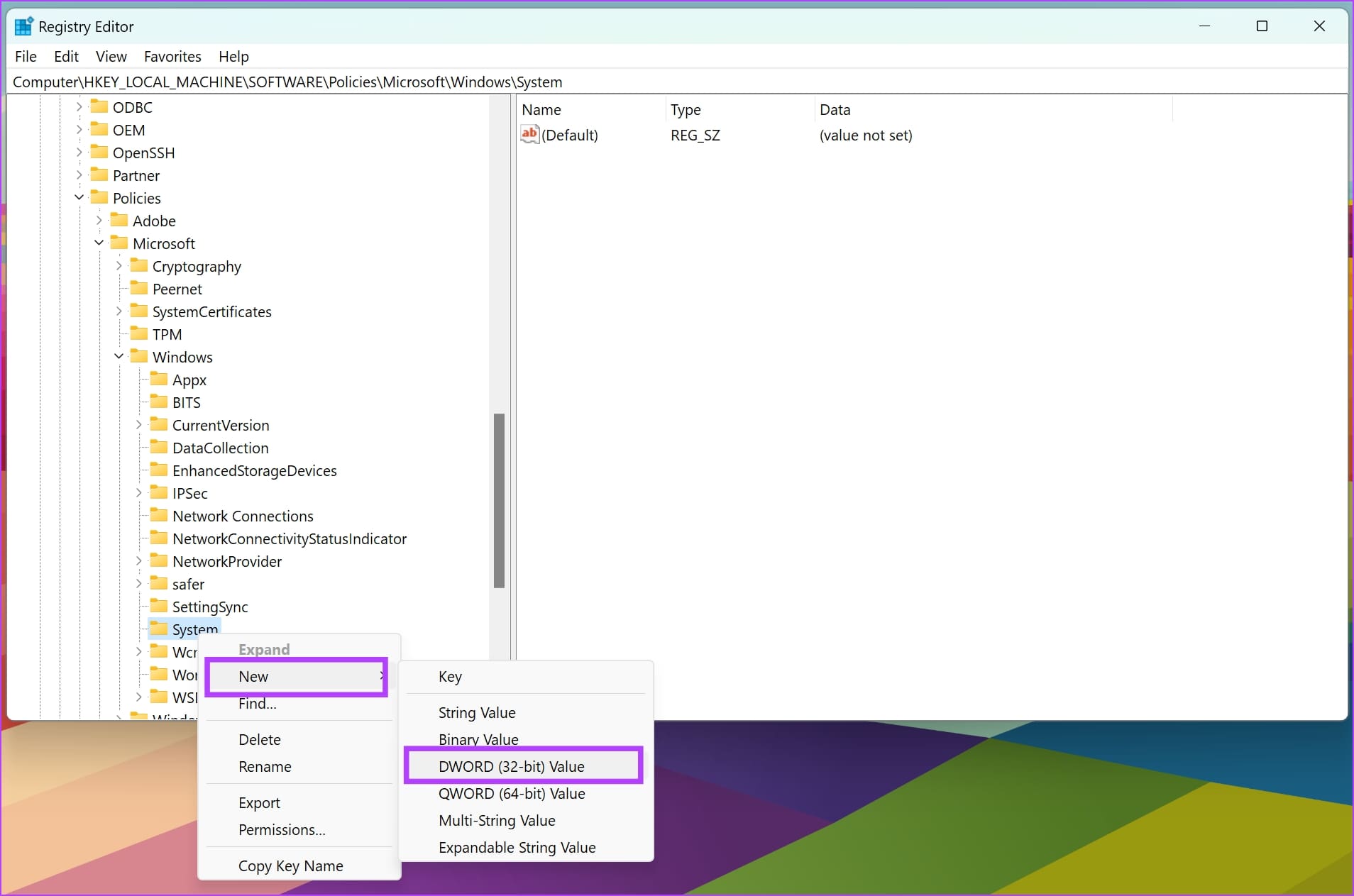
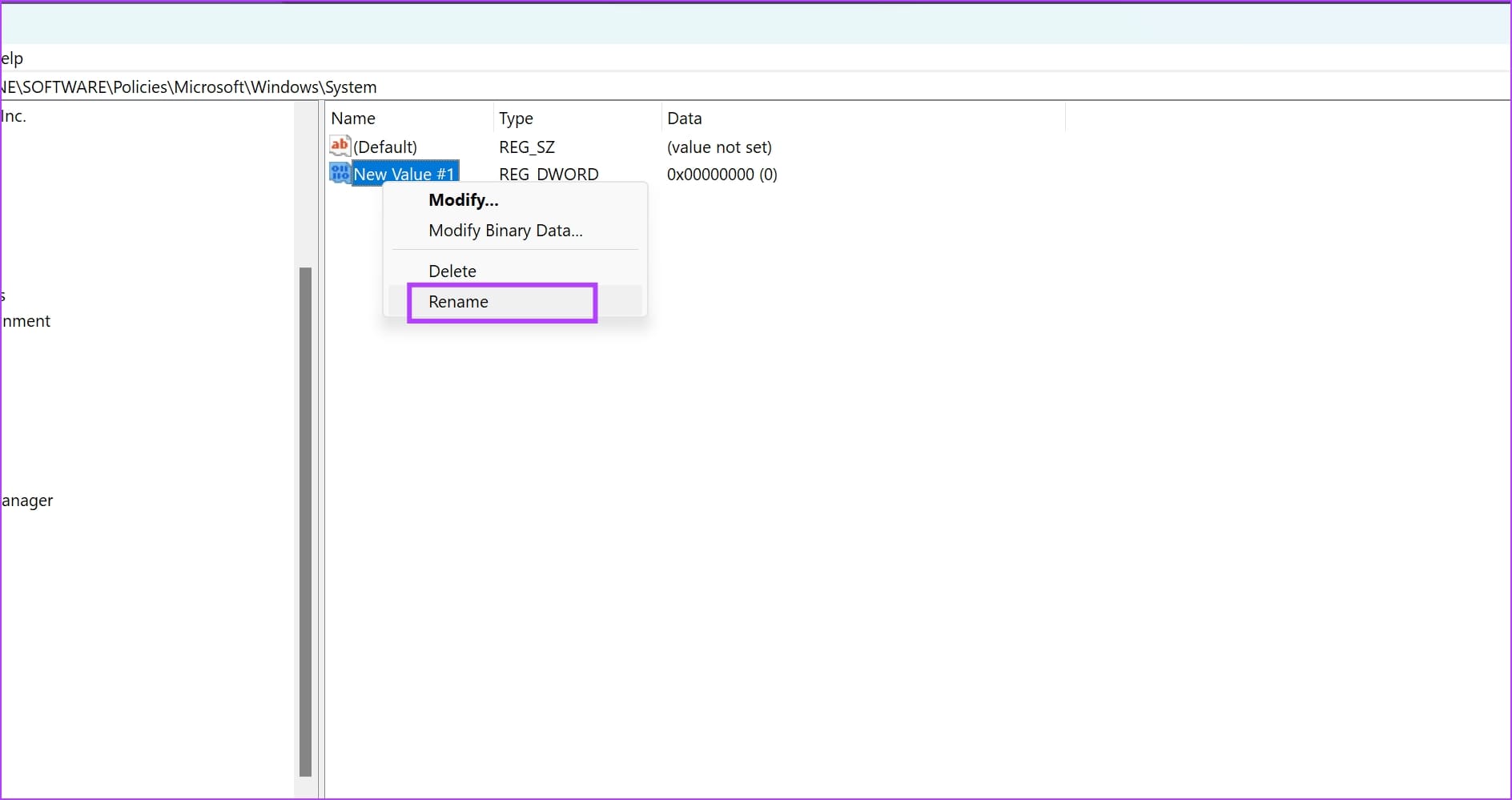
Step 6: Right-click on the new entry and click on Rename .
Enter the new name as AllowDomainPINLogon .
Step 7: Double-click on the new entry.
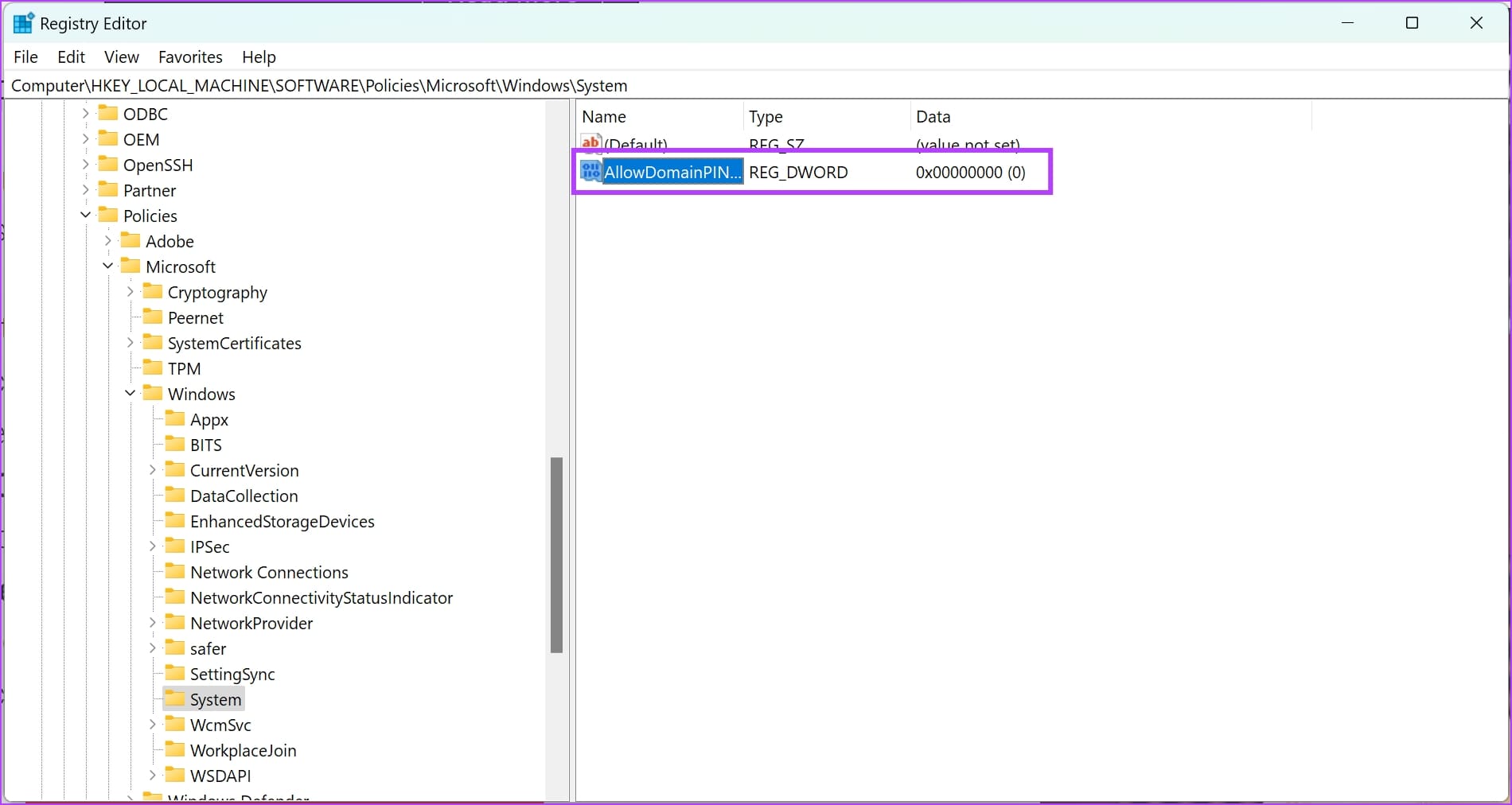
Step 8: Enter 1 in the value data. Click on OK .

Fix 6: Troubleshoot Hardware Devices
Running the hardware troubleshooting service on your Windows PC can fix issues with the fingerprint scanner.
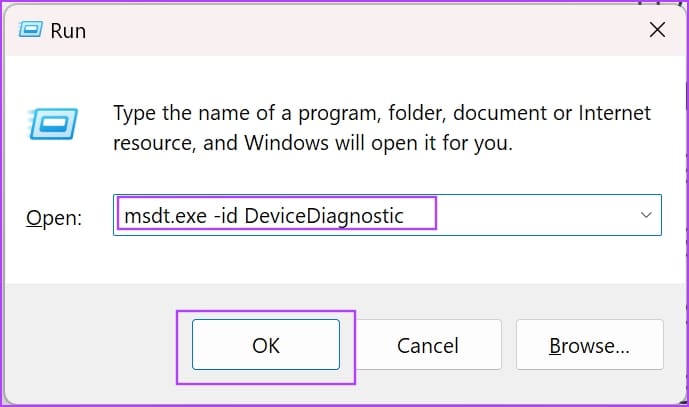
Step 1: Open the Run window on your PC.
Step 2: Enter the following command, and click on OK to open the hardware diagnostics service.
msdt.exe -id DeviceDiagnostics
Step 3: Click on Next , and the troubleshooting will begin. Once it is complete, follow the on-screen instructions to take the relevant actions.