- Checking the system files and repairing the Visual C++ Redistributable packages can help fix this error.
- If this error only affects a specific app or program, review its permissions or try reinstalling it on your PC.
- If the error persists, try re-registering the problematic DLL file using Command Prompt or perform a system restore.
Try Basic Fixes
- Update or reinstall the problematic software: Compatibility issues with your app or program can trigger the “DLL is not designed to run on Windows” error on your PC. If this error only affects a specific app or program, try updating or reinstalling it and see if it helps.
- Scan for malware: The presence of malware on your PC could also prevent DLL files from running correctly on your Windows 10 or 11 PC and cause such problems. To overrule this, run a full system scan using Windows Defender or a reliable third-party antivirus program.
- Install Windows updates: Microsoft frequently releases updates for your Windows PC to add new features, improve performance, and fix bugs and issues. It’s a good idea to install any pending Windows Updates and see if that helps.
Fix 1: Check for Permission Issues
A lack of necessary permissions is a common reason you may encounter the “DLL is not designed to run on Windows” error while running an app or program. Here’s how to fix that.
Step 1: Click the search icon on the taskbar, type the name of the program that’s giving you the error, and select Open file location .

Step 2: Right-click on the .EXE file of the program and select Properties .

Step 3: Under the Security tab, click the Edit button.

Step 4: Select Users and tick the Allow checkbox for Full control . Then, hit Apply > OK .

Fix 2: Run the SFC and DISM Scans
Corrupt or damaged system files on your computer can also cause such errors. You can run the built-in SFC (System File Checker) and DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) scans to fix the damaged files causing the error.
Step 1: Right-click on the Start icon and select Terminal (Admin) from the list.
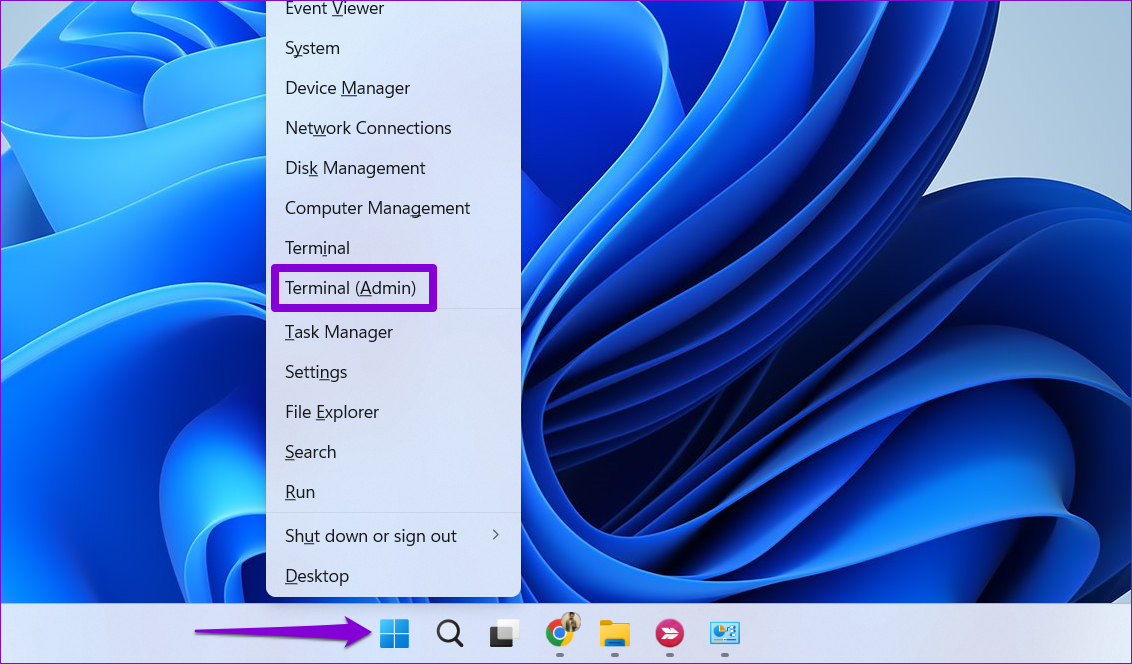
Step 2: In the console, type the following command and press Enter .
SFC /scannow

Step 3: Run the following commands one by one and press Enter after each one to run the DISM scan:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealthDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealthDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

Now, restart your PC to check if the issue persists.
Fix 3: Repair the Visual C++ Redistributable Packages
Several popular Windows apps and programs rely on Visual C++ runtime libraries to provide essential features and operate smoothly. However, if there is a problem with the Visual C++ redistributable package on your computer, you may get the error “DLL is not designed to run on Windows” while opening or using a program. Here’s how to can fix that.
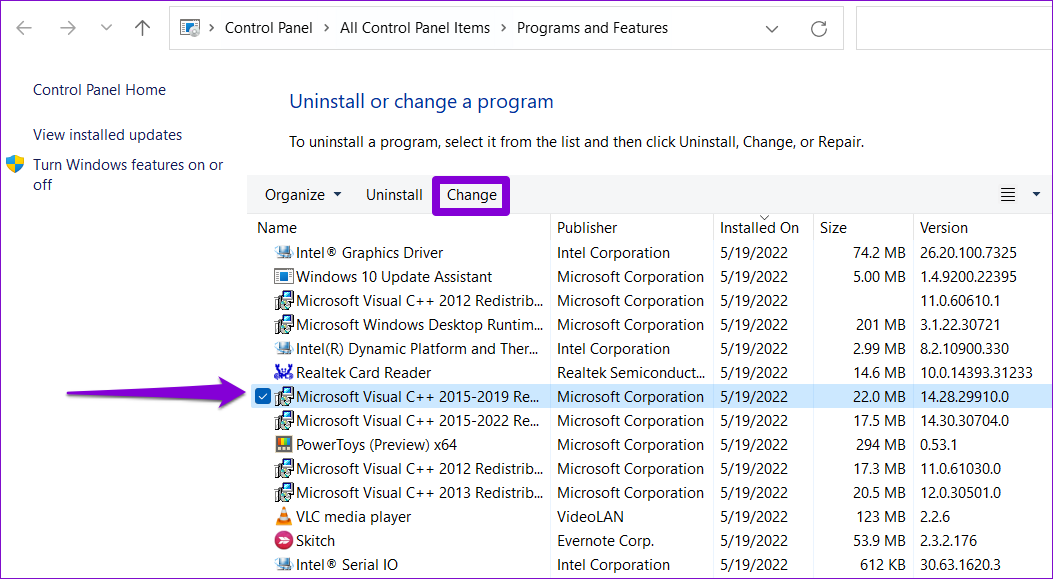
Step 1: Press the Windows + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run dialog box. Type appwiz.cpl and press Enter .
Step 2: Select the Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable package and click Change . Repeat this process to repair all the packages.
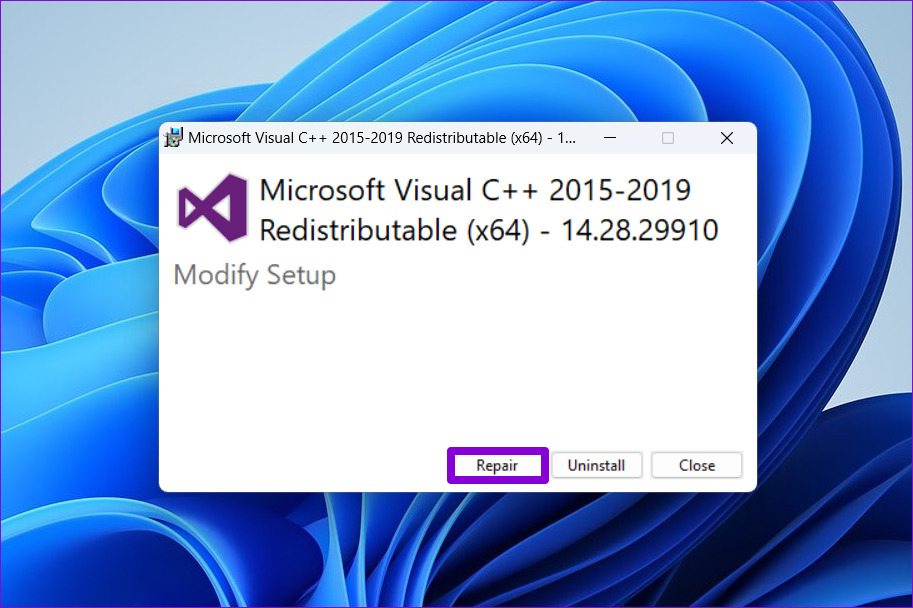
Step 3: Hit the Repair button and wait for the process to complete.
Fix 4: Re-Register the Problematic DLL File Using Command Prompt
Another thing you can do to resolve this error is to re-register the problematic DLL file. Here’s how:
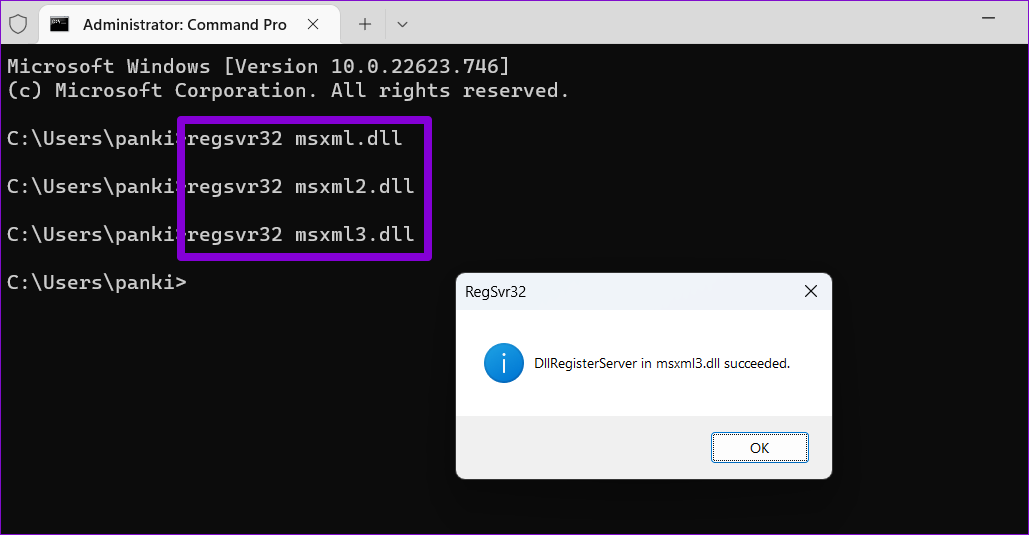
Step 1: Right-click on the Start icon and select Terminal (Admin) from the list.
Step 2: In the console, type regsvr32 , followed by the name of the DLL file. For instance, if you were to re-register the msxml3.dll file, your command would be this:
regsvr32 msxml3.dll
Exit the Terminal window and check if Windows still shows the error.
Fix 5: Perform a System Restore
Lastly, if the “DLL is not designed to run on Windows” error has only started appearing recently, use system restore to revert your PC to a point when it was working properly. Here’s how.
Step 1: Click the search icon on the taskbar, type create a restore point , and press Enter .

Step 2: Navigate to the System Protection tab and click the System Restore button.

Step 3: Select the Recommended restore option and click the Next button at the bottom.

Step 4: Click Finish and allow Windows to restore to the specified restore point.
