- Windows 11 gives many options for configuring RAID 1, including using the Settings app and the Command Prompt.
- Using the Settings App is the most direct way to configure RAID 1.
Hardware Requirements for a Raid Set Up
Before you go into creating RAID 1 on Windows 11, take note of the following requirements:
- You should have a minimum of two drives.
- All drives involved need to have the same file type – NTFS works great.
- There must be a RAID controller; on Windows 11, you may use the built-in Storage Spaces feature as a software alternative.
- A motherboard that is compatible with RAID. This may be a problem for older motherboards.
Method 1: Via the Settings App
The Settings app is a central location that allows you to configure multiple operating system options. From appearance and behavior personalization to managing privacy and security, the app can accomplish so much. You may also use it to configure RAID options and create RAID 1, as shown below.
Step 1: Press the Windows + I keyboard shortcut on your keyboard to open the Settings app.
Step 2: Click the Storage option on the right pane.

Step 3: Scroll down the right pane and click Advanced Storage Settings .

Step 4: Click Storage Spaces on the right pane.
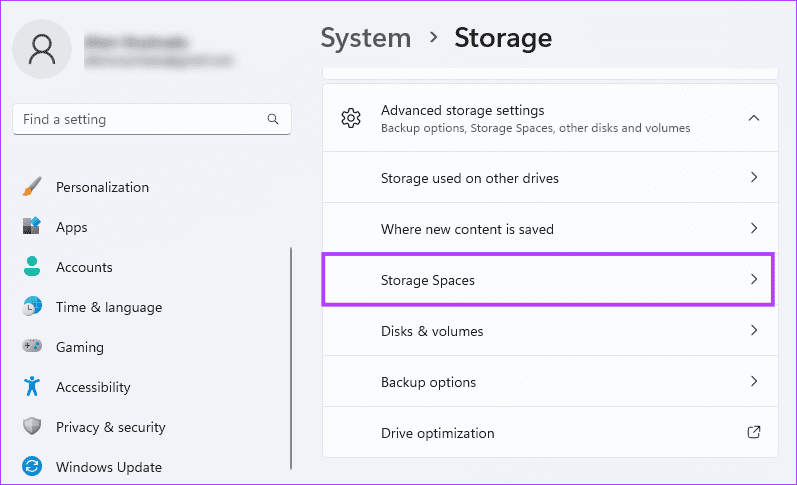
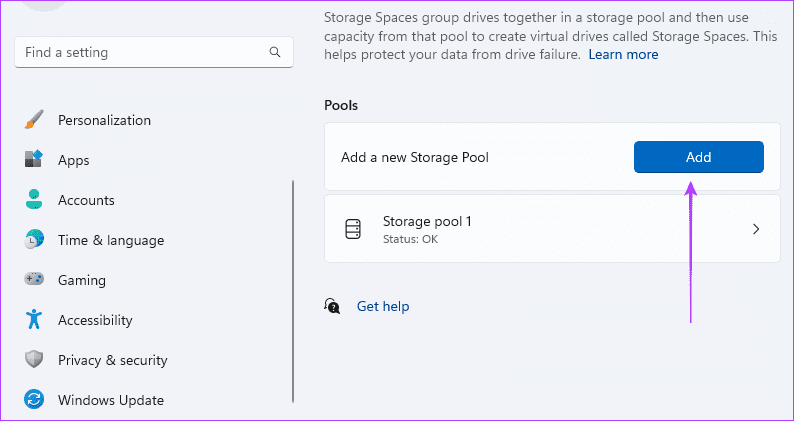
Step 5: Click the Add button to create a RAID storage.
Step 6: Fill in the Name field, select the disk from which you want to create RAID 1, then click the Create button.

Step 7: Here, you fill in details for the space to which the pool in the previous window will belong. Enter a value for Name , pick the size you desire, select Two-way mirror for Resiliency , and click Create .

Method 2: Using the Control Panel
Control Panel is a utility that allows users to change and reconfigure certain options on the device. It comprises hardware and software configuration applets and may be used to manage specific drive functions, like creating RAIDS, as shown below.
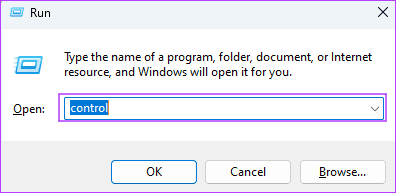
Step 1: Press the Windows + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run dialog, type control , and hit Enter .
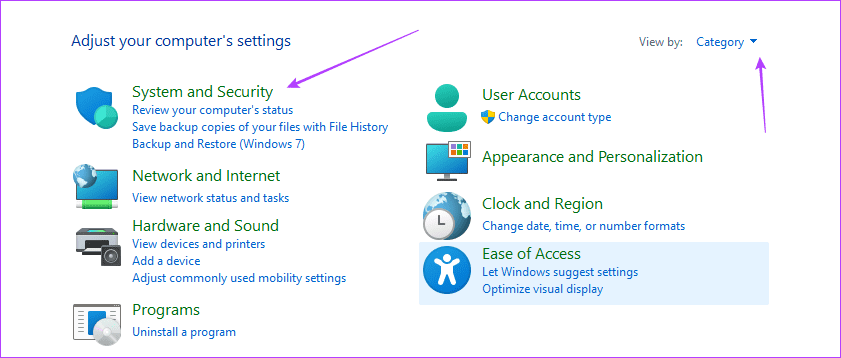
Step 2: In the top-right corner, make sure the View by option is set to Category and click System and Security .
Step 4: Click Storage Spaces .

Step 5: Click Create a new pool and storage space .

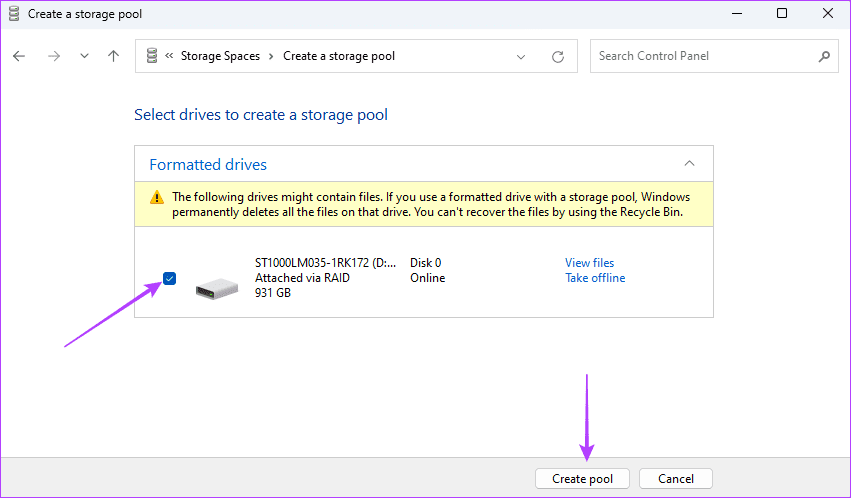
Step 6: Select your drive and click Create Pool .
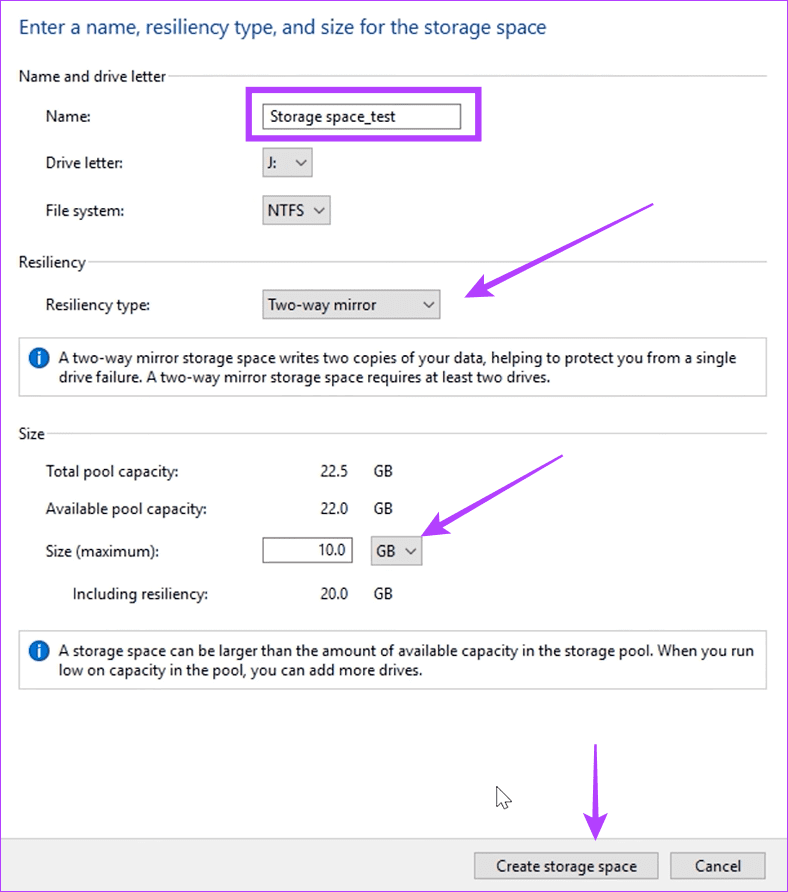
Step 7: Name the Storage Space. Use the drop-down next to Resiliency type to choose Two-way mirro r, select an appropriate size, and then click Create storage space .
Method 3: From the Disk Management Settings
On Windows 11, you may use the Disk Management utility to manage hard drives and disks. The tool lets you create, resize, delete, format, and manage the drives on your computer. You may also employ this tool to create RAID 1 on Windows 11.
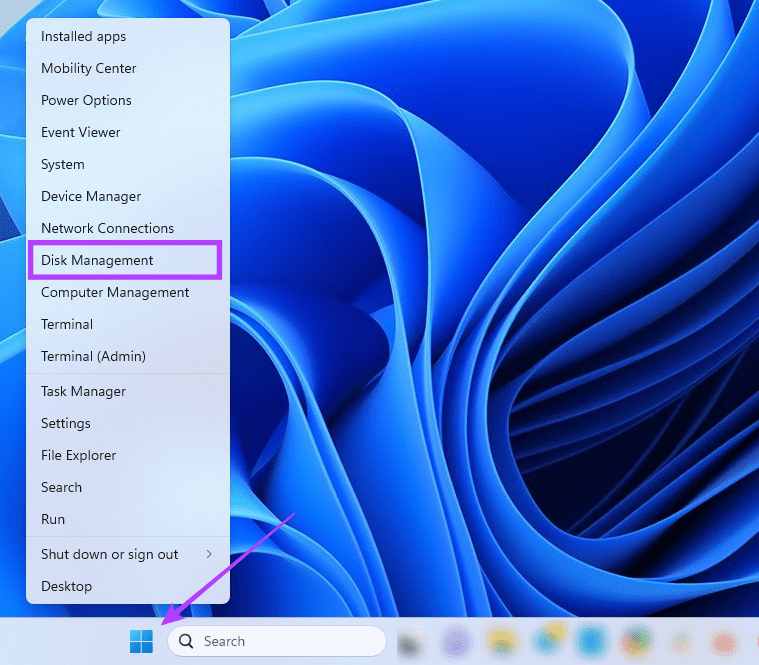
Step 1: Right-click the Start menu on your Taskbar, then select Disk Management .
Step 2: Right-click on the Drive for your RAID, and select New Striped Volume .
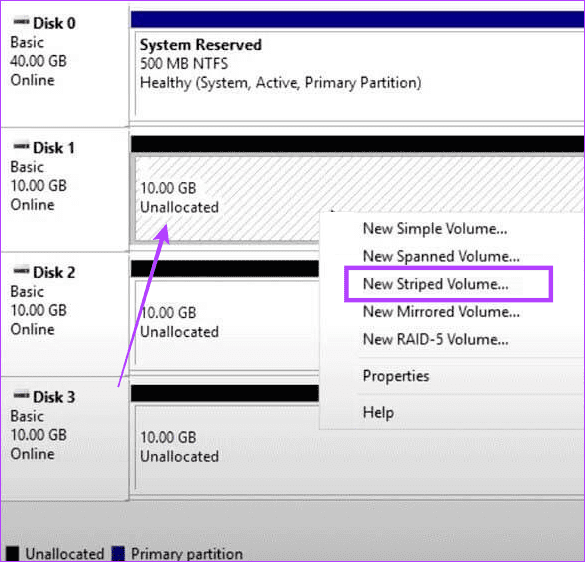
Step 3: Click Next .
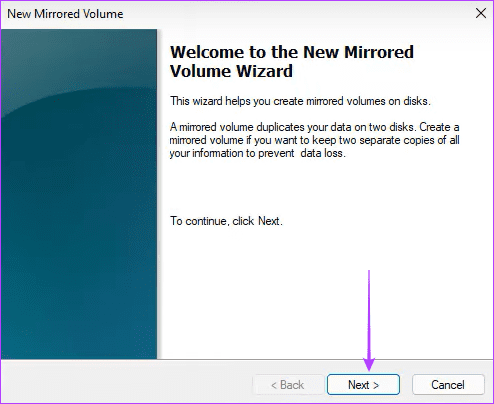
Step 4: Select the disk to RAID, click Add , then click Next .
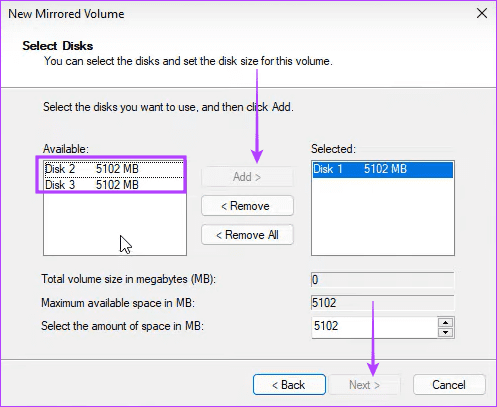
Step 5: Select NTFS and click Next .
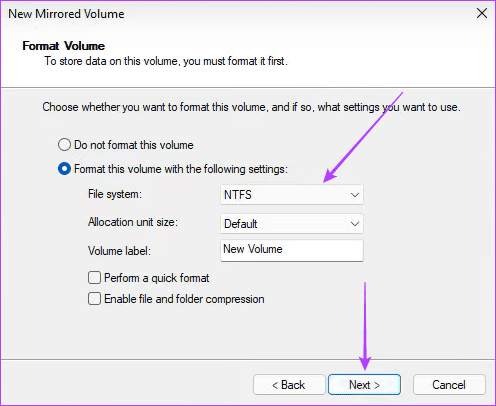
Step 6: Click Finish and confirm your choice.
Method 4: Using the Command Prompt
The Command Prompt is a text-based interface allowing users to interact with the Windows operating system. It is a powerful tool that may be employed for system configuration, file management, troubleshooting, or even disk management. As shown below, you may use it to create a RAID 1 drive.
Step 1: Press the Windows + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run dialog.
Step 2: Type cmd and hit Control + Shift + Enter keyboard shortcut to open the Command Prompt with admin privileges.

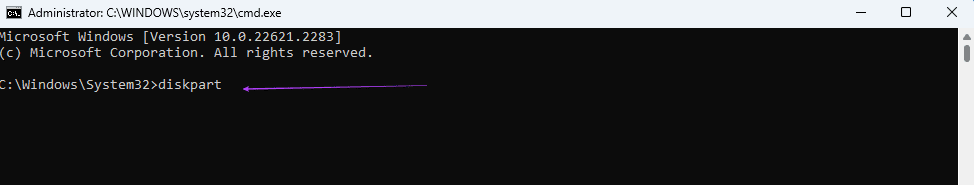
Step 3: Type the below command and hit Enter to access drive and disk management:
diskpart
Step 4: Run the below command to see all available drives:
listdisk

Step 5: Run the command below, replacing N with a disk number for the RAID:
Select disk N
Step 6: Run the command below to convert the selected drive to a dynamic one:
convert dynamic
Step 7: Repeat steps 5 and 6 for other drives you need to be part of the RAID process.
Step 8: Enter the command below to create your RAID volume:
Create Volume RAID Disk 1, 2, 3

Step 8: Select the newly created RAID using the command below:
select volume 2
Step 9: Change the format and assign it a drive letter by running the two scripts below one after the other:
Format FS=NTFS Label=NewVolume
Assign Letter=E

Was this helpful?
- In most cases, running the printer troubleshooter or configuring the “Print Spooler Service” should resolve the error.
- Deleting old printer devices and print spooler files can also help fix the issue.
- If nothing works, you may need to delete corrupted print spooler registry entries.
Fix 1: Run Printer Troubleshooter
Windows comes with a dedicated printer troubleshooter that can automatically diagnose and fix any printing issues on your PC. It checks all of your printer configurations and corrects any inconsistencies. Here’s how to run it.
Step 1: Press the Windows key + I to launch the Settings app and head to System > Troubleshoot .
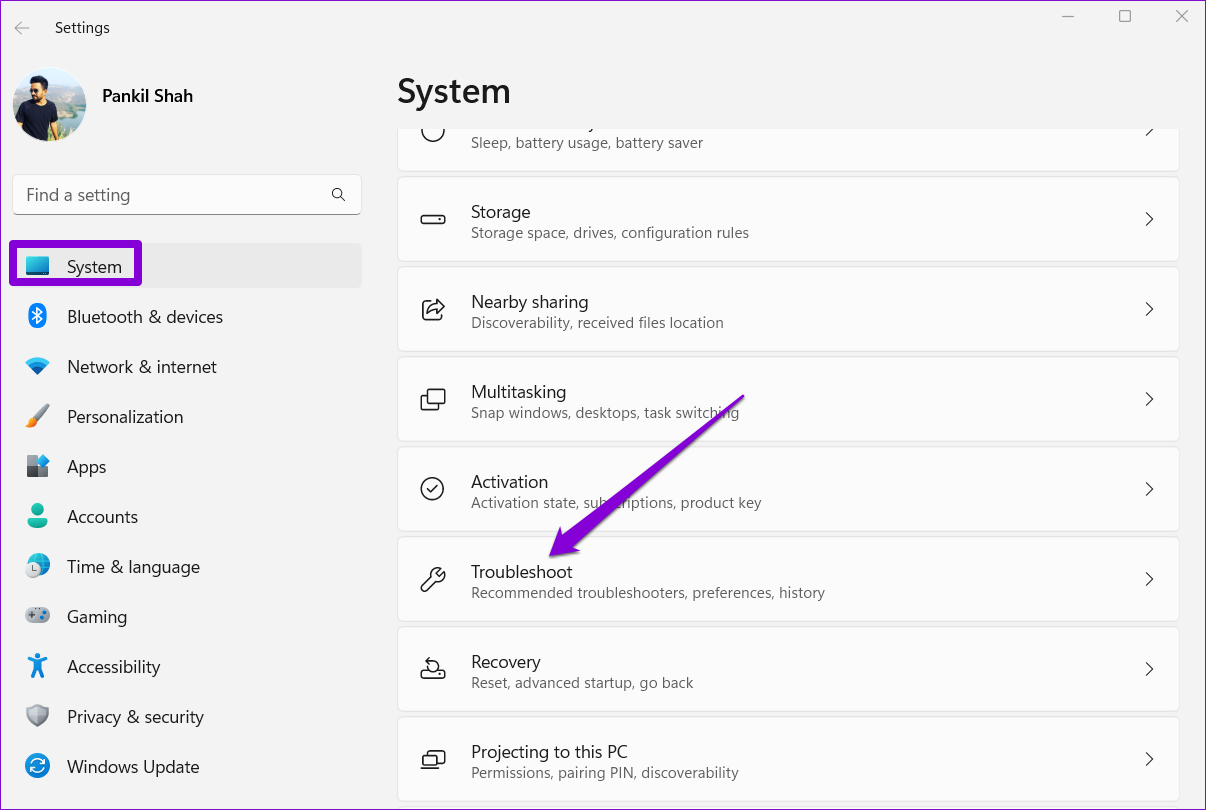
Step 2: Go to Other troubleshooters .
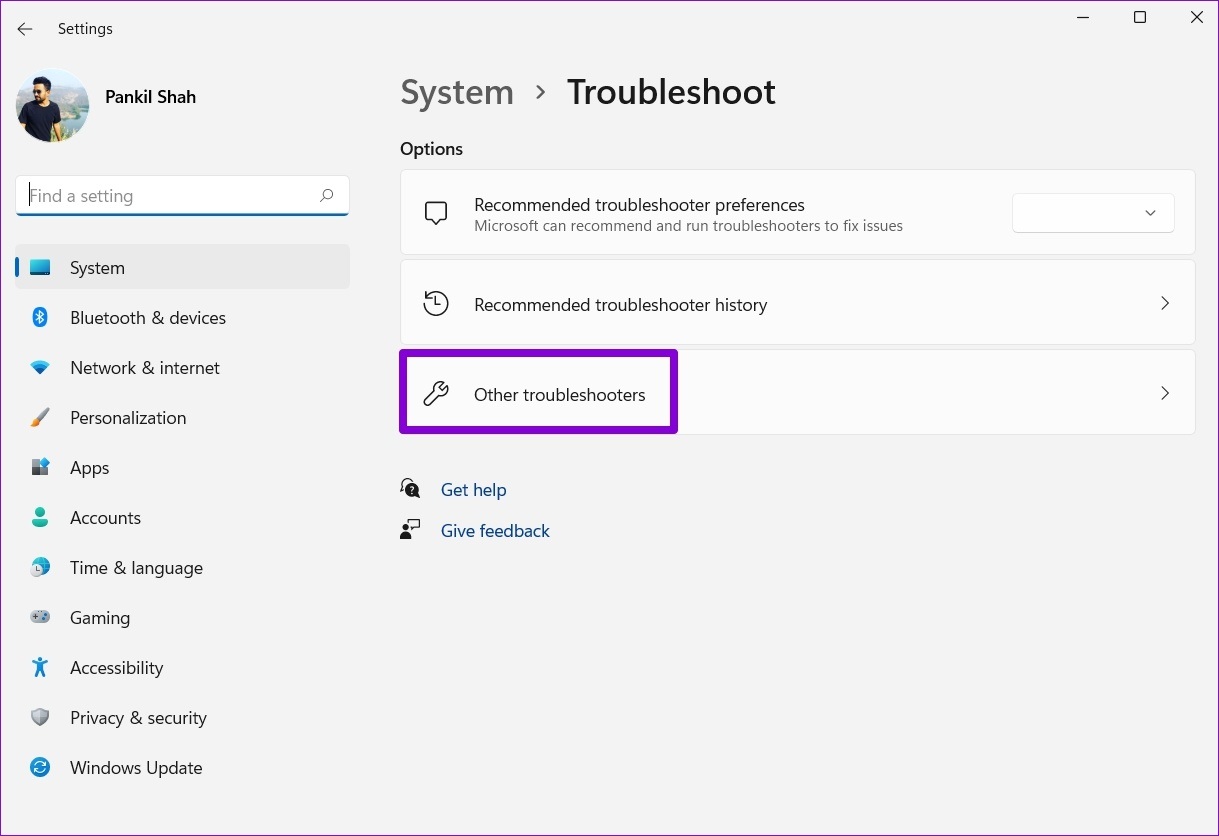
Step 3: Click the Run button next to Printer to begin troubleshooting.
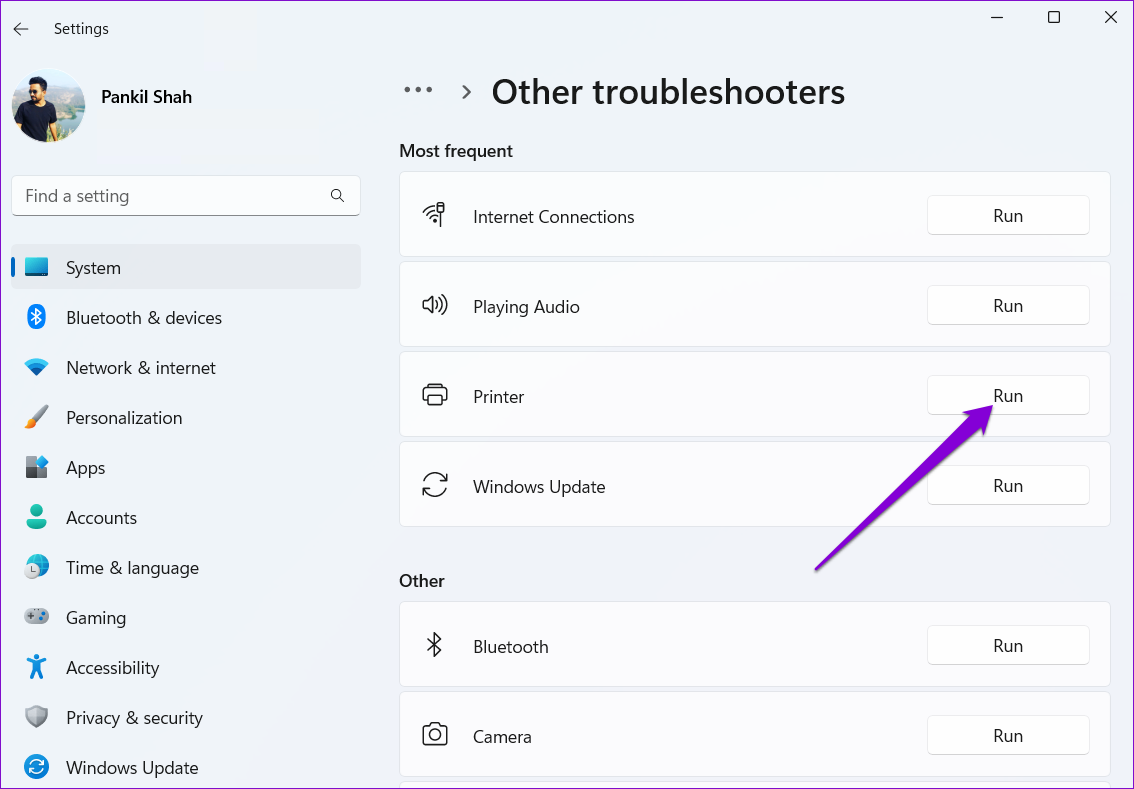
From there, follow the on-screen prompts to finish the troubleshooting process.
Fix 2: Check Print Spooler Service
If the Windows troubleshooter fails to identify any issues, you can check the Print Spooler service on Windows to see if it is properly configured. Here’s how.
Step 1: Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog. Type services.msc in the box next to the Open field and press Enter .
Step 2: In the Services window, scroll down to locate Print Spooler . Right-click on it and select Properties .
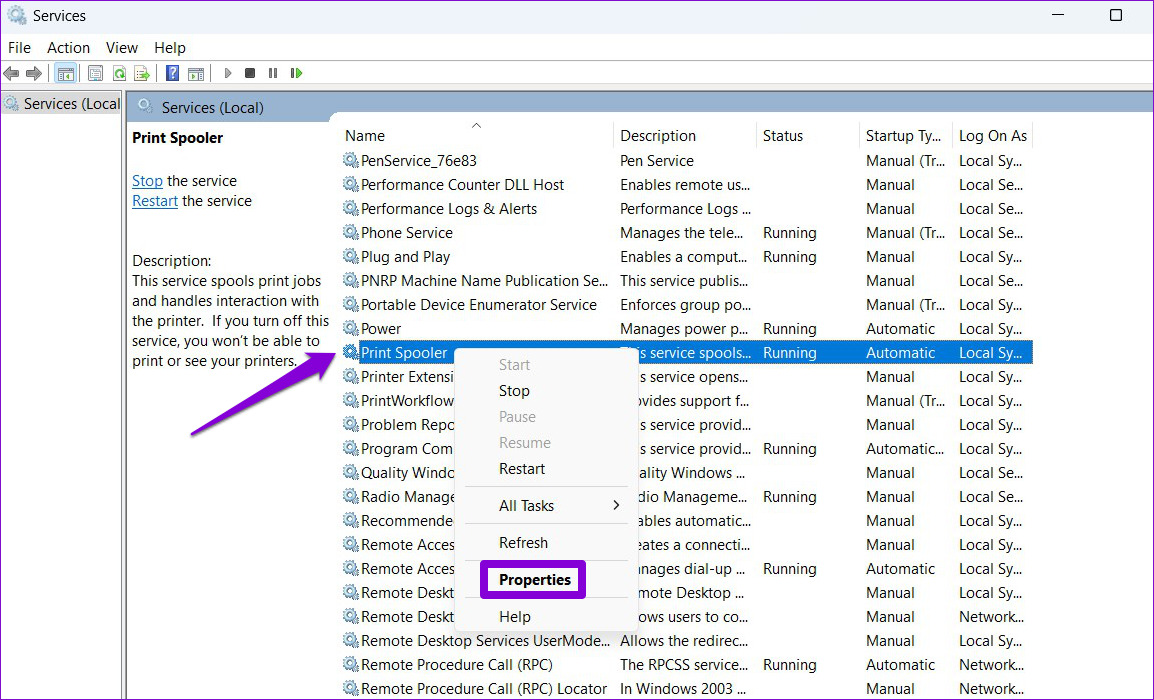
Step 3: Set the Startup type to Automatic from the drop-down, if it isn’t set already.
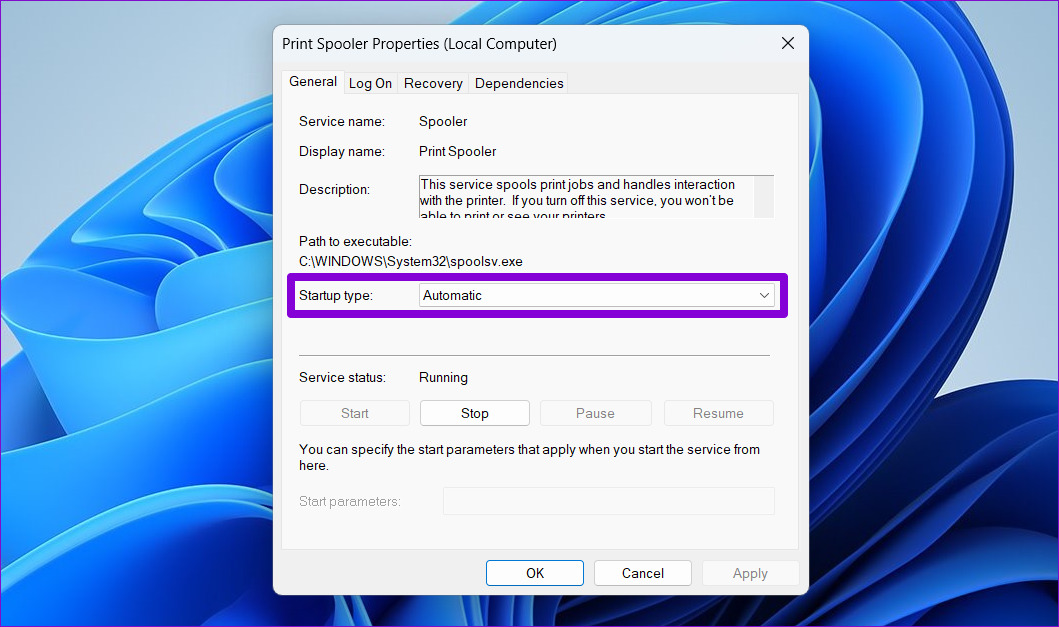
Step 4: On the Recovery tab, use the drop-down menus next to First failure, Second failure, and Subsequent failures to select Restart the Service . Then, click on Apply followed by OK .
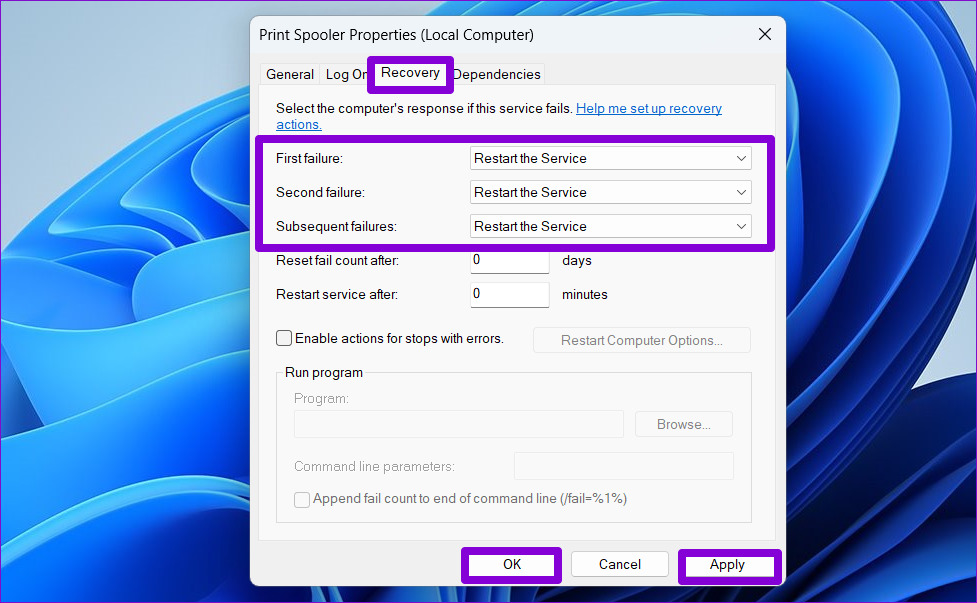
Restart your PC and check if the print spooler stops again.
Fix 3: Remove Old Printers
Sometimes, the print spooler service may also stop working if several printers are connected to your PC. You can try deleting some of your old printer devices to see if that helps.
Step 1: Click on the search icon on the taskbar, type in printers & scanners and press Enter .
Step 2: Select the printer you want to remove.
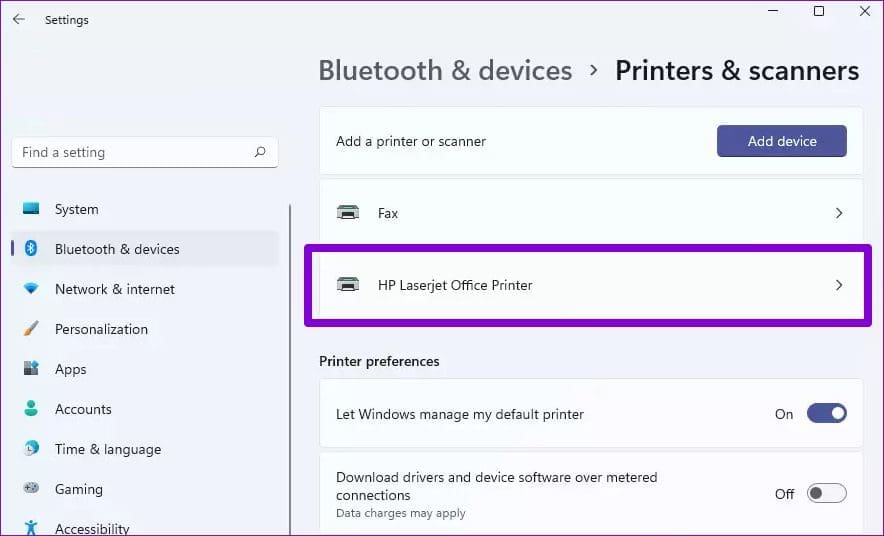
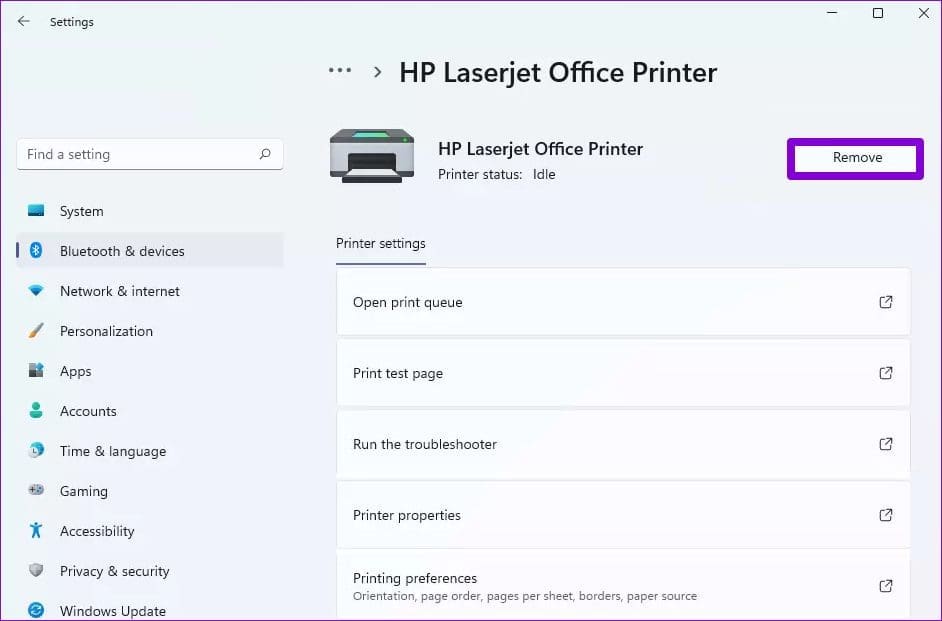
Step 3: Click on the Remove button in the top right corner. Repeat this process to remove unwanted printers and try using the printing services again.
Fix 4: Delete Old Print Spooler Files
Existing print spooler cache data can also interfere with the service and cause it to crash repeatedly when corrupted. In that case, you can delete those old print spooler files to fix the issue.
Step 1: Press the Windows key + S to open Windows Search. Type services in the box and select the first result that appears.
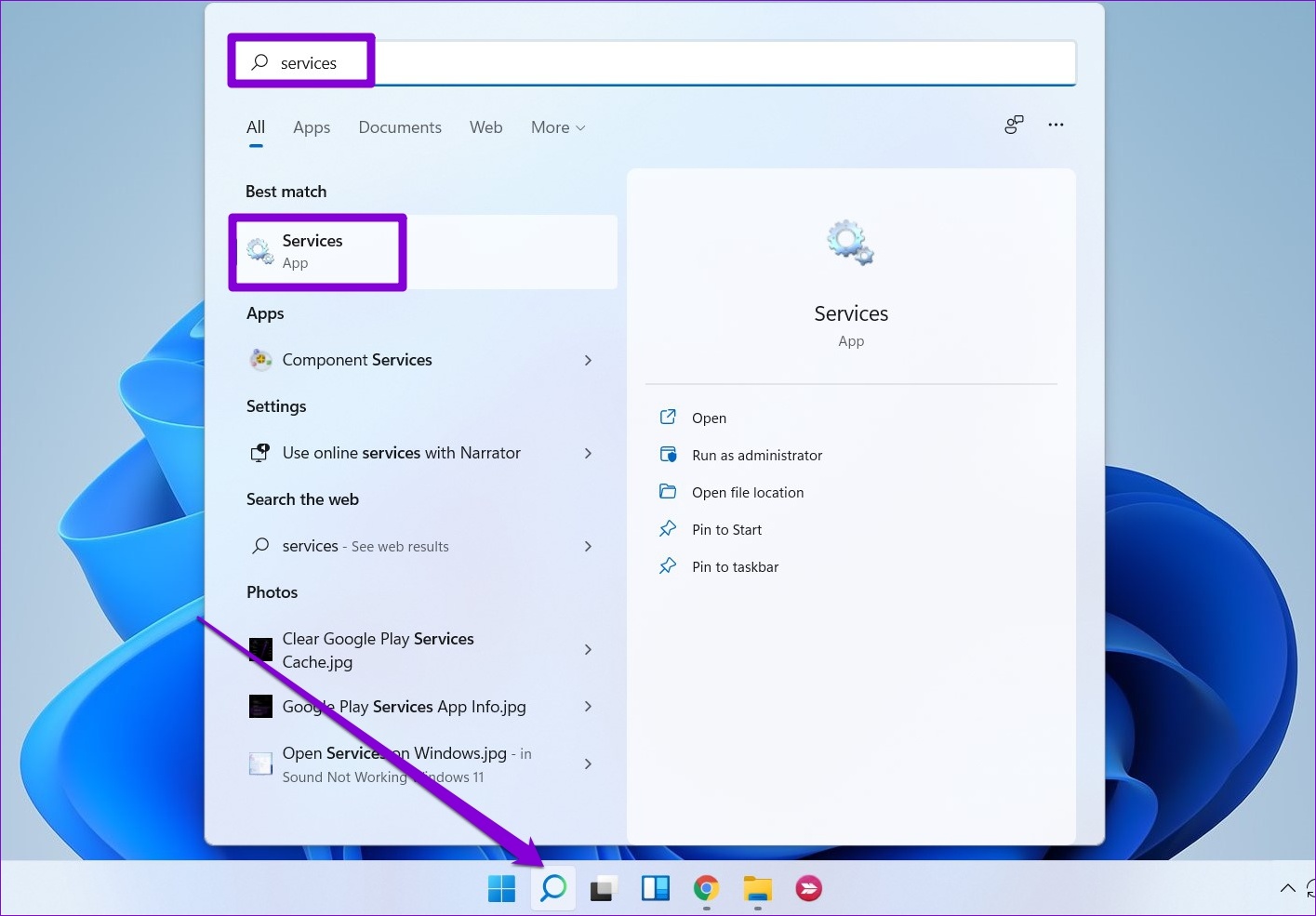
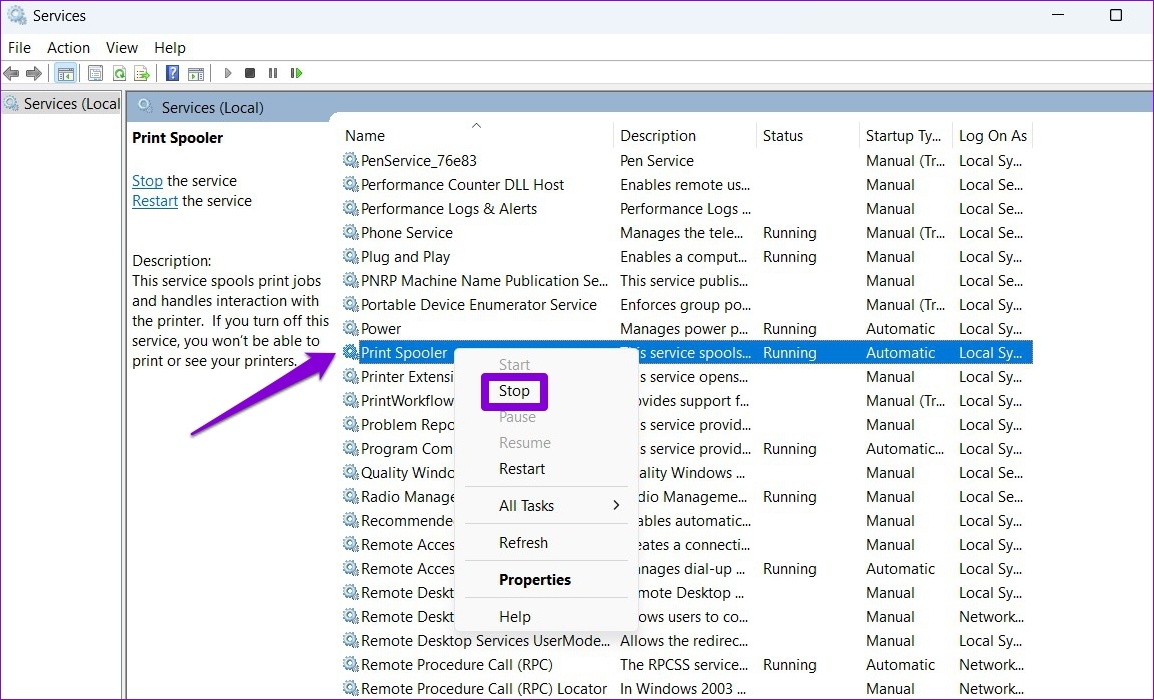
Step 2: Right-click on Print Spooler and select Stop .
Step 3: Press the Windows key + E to launch File Explorer on your PC and navigate to the following folder:
C:\Windows\System32\spool\PRINTERS
Step 4: Select all folders and click on the trash icon at the top to delete them.
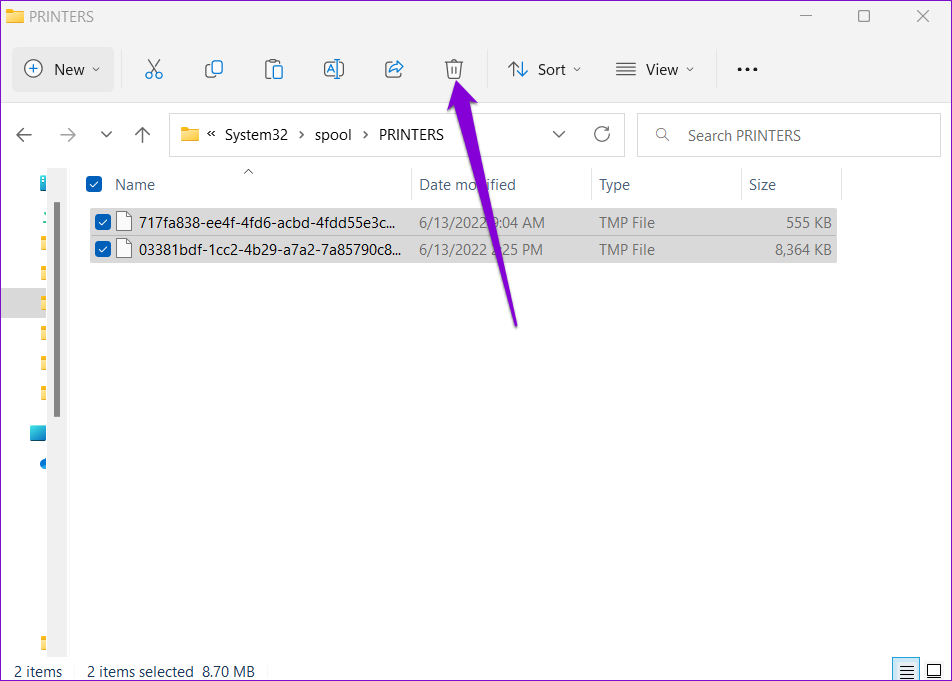
Restart your PC after you delete the files. The print spooler service should start automatically upon reboot.
Fix 5: Update Printer Drivers
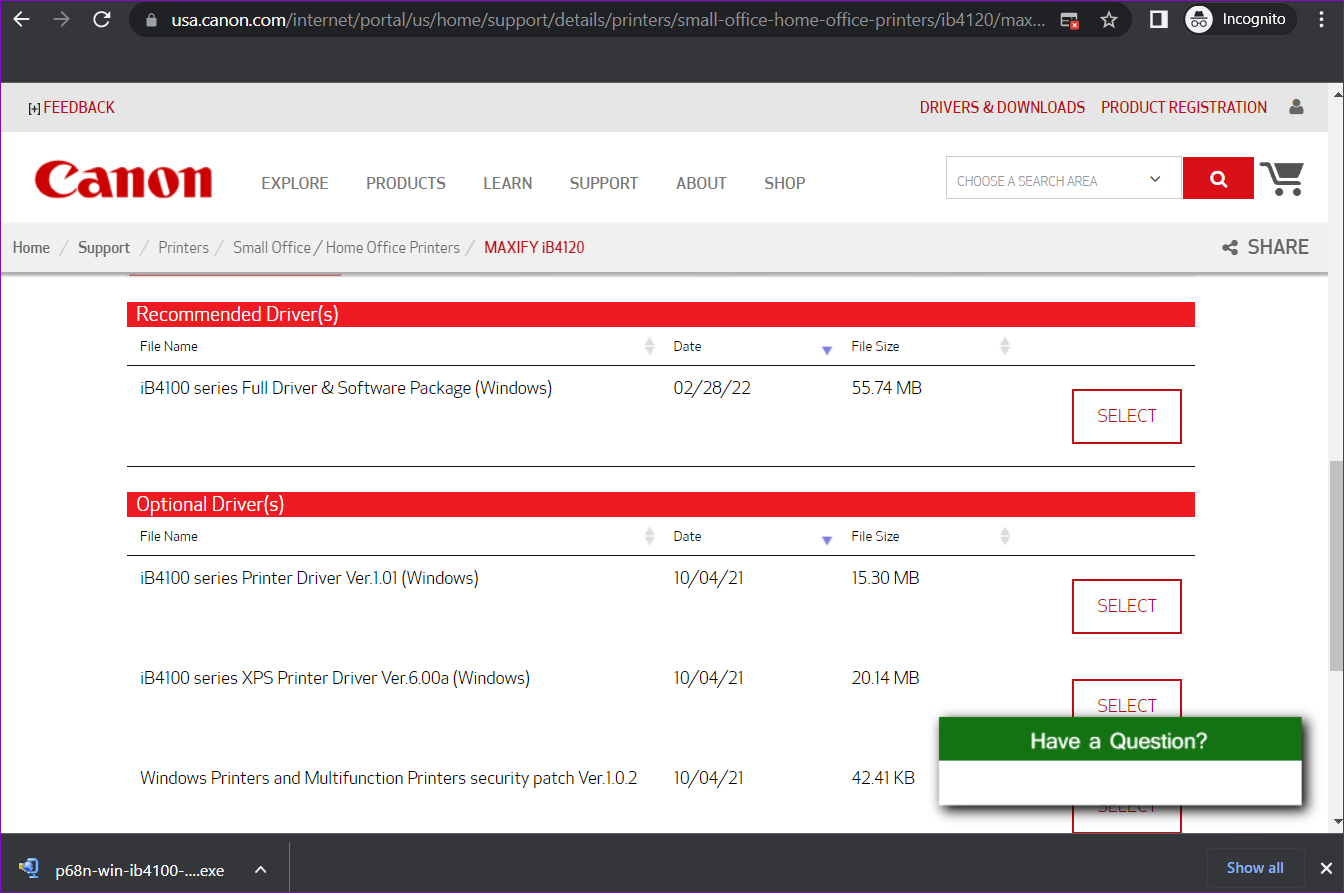
Issues with your current printer drivers can also cause the print spooler to stop abruptly. If the printer drivers on your PC are outdated or corrupted, then updating them should help more often than not.
To update printer drivers, download the most recent drivers from the respective manufacturer’s website. Then, open the downloaded file to begin the installation.
Fix 6: Delete Print Spooler Registry Keys
If none of the above solutions work, you can try deleting a few registry keys associated with the print spooler. Here’s how:
Step 1: Press the Windows key + R to launch the Run dialog box. Type regedit in the box and press Enter .
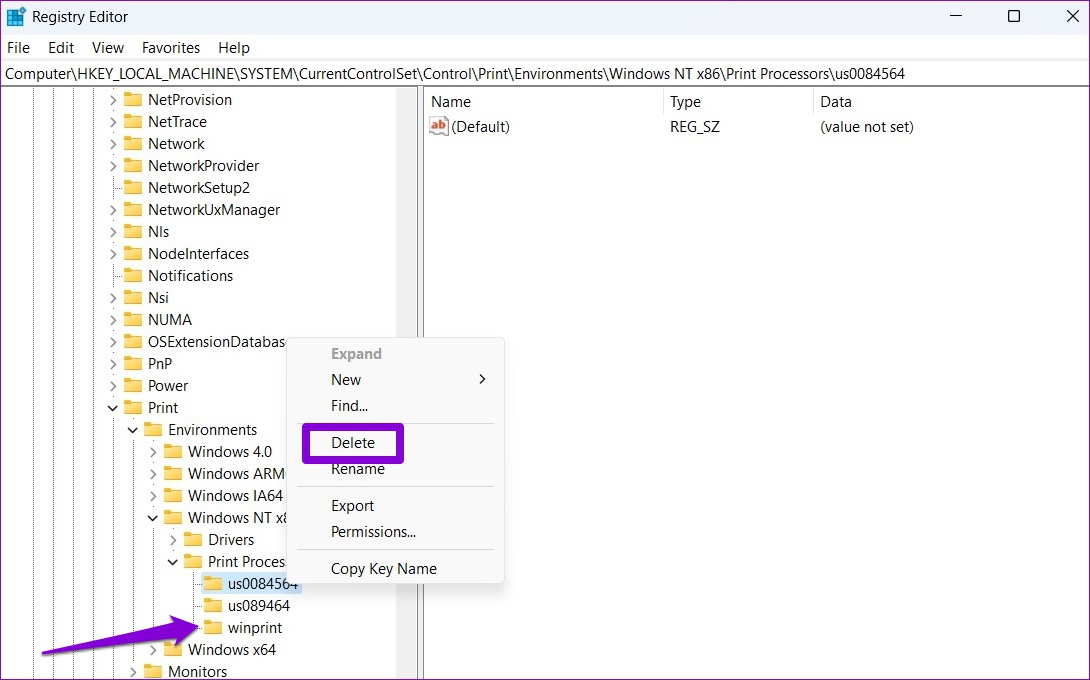
Step 2: Paste the following path in the address bar at the top to navigate to Print Processors:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Print\Environments\Windows x64\Print Processors
If you’re using a 32-bit version of Windows, use the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Print\Environments\Windows NT x86\Print Processors
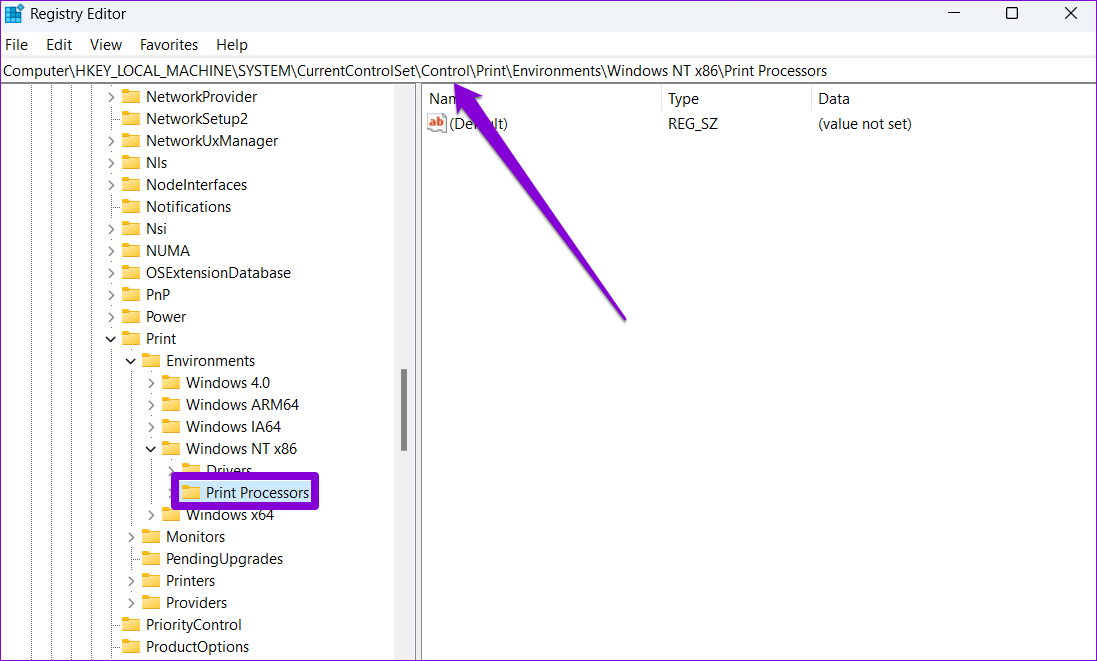
Step 3: Delete all keys inside Print Processors except winprint . To delete a key, right-click on it and select Delete . Click on Yes on the prompt.